Total Quality Management ensures maximum effectiveness and efficiency within a business and secures commercial leadership by putting in place process and systems which will promote excellence and prevent errors. It ensures that every aspect of the business is aligned to the customer needs and the advancement of business goals without duplication or waste of efforts. Different companies have different approaches to implement Total Quality Management (TQM). The following principles (which are common to all companies) must be adhered for the successful Total Quality Management (TQM) implementation: Continuous improvement. TQM is a long-term process that entails achieving improvements in the company’s operations. This means that management should establish targets for improvement and measure progress by using reliable criteria. The quest for quality and better service to the customer should be a continual, never-ending one. Competitors will seek to provide better service and customers will come to expect it. Hence, to cease Continue reading
Operations Management
Concept of Vendor Management
Vendor Management is the management and control, by an entity, of those third parties that supply goods and/ or services to that entity. It is the discipline of establishing service, quality, cost, and satisfaction goals and selecting and managing third party companies to consistently meet these goals:- Establishing Goals– Just as employees need clearly established goals, operations need clearly defined performance parameters. When selecting or managing vendors, vendor managers must optimize their opportunity to achieve these goals by using third parties companies. Selecting Vendors– The fine art of vendor management is essential to optimizing operational results. Different vendors have different strengths and weaknesses, and it is the vendor manager’s responsibility to match the right company with the desired performance characteristics. Failure to consider this comprehensively could lead to complete failure. Managing Vendors– On a daily basis, vendor managers must monitor performance, provide feedback, champion new projects, define Continue reading
Types of Inventory System (Q and P Models)
The term inventory derives from the French word inventaire and the Latin word inventariom which simply means a list of things which are found. The term inventory includes materials which are in raw form, or are in process, in the finished packaging, spares and the others which are stocked in order to meet all the unexpected demands or distribution in the future. This term usually refers to the stock at hand at a particular period of time of all those materials which are in raw form, those goods which are in progress of manufacture, all the finished products, merchandise purchased products for resale of those products, tangible products which can be seen, touched, measured or are countable. In a connection with the financial statements and records of accounting, the reference may be to the amount assigned to the stock or the pile of goods owned by an enterprise at a Continue reading
Importance of Customer Service in Supply Chain Management
Supply chain is basically considered as a strategic concept that involves understanding and managing the sequence of activities -from supplier to customer-that add value to the product supply pipeline. The role of customer service in the supply chain management is not incidental. Every company in this chain, irrespective of market size mainly they thankful to its customers as the fact is that in all profit of firm there are customers are in center whom to buy the goods and services produced by each one of them. This century marks the end of monopolies and therefore customers can make an array of choices. When customers decide not to buy products in a particular supply chain, then no doubt the company would collapse without earning any revenue for the expenses incurred in launching the product on the stage of saturation and decline stage. So, the supply chain should be structured in such Continue reading
Types of Purchasing Systems
The effectiveness of purchasing activities can be enhanced by proper organization and coordination of the activities. There are four types of purchasing system:- Purchase made as per requirement: No purchase is made in advance. Purchase is done as need arises. Method usually applied for emergency requirement or infrequent goods. Contract Purchasing: Contract of material is given to an agency. It has an advantage that low price of those materials whose cost fluctuates highly. Market Purchase: Purchase is made from the market to take advantage of price fluctuations. Schedule Purchasing: It is a cyclic purchase model. A schedule of purchase is made and it is used for those commodities whose price do not fluctuate. Centralized purchasing means buying and managing purchases from one location for all locations within an organization. This can also be run by a central location buying in to a distribution warehouse that feeds smaller warehouses. This is Continue reading
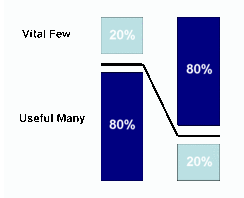
Quality Management Tools: Pareto Analysis
Pareto analysis is a very simple technique that helps a manager to choose the most effective changes to make. It is represented as a bar graph used to arrange information in such a way that priorities for process improvement can be established. Pareto charts are constructed to provide a before-and-after comparison of the effect of control or quality improvement measures. The Pareto Effect The 80:20 theory was first developed in 1906, by an Italian economist, Vilfredo Pareto, who observed an unequal distribution of wealth and power in a relatively small proportion of the total population. This fact gave rise to the Pareto effect or Pareto’s law: a small proportion of causes produce a large proportion of results. Thus frequently a vital few causes may need special attention wile the trivial many may warrant very little. It is this phrase that is most commonly used in talking about the Pareto effect Continue reading