First, it is necessary to understand why the field of cross-cultural differences is vital to business interactions. In many situations, it is beneficial for companies to merge. Some businesses are failing to perform on their own, but still possess resources that may be valuable for businesses in the same sphere. Other companies aim to expand to increase their growth and support the rising demand for their services. Overall, joint ventures and alliances happen to raise the value of the merging entities, whether this value is connected to the brands presence, technologies and other resources or economies’ scaling. Cross-border acquisition and merger can be motivated by these factors as well – companies often want to enter new markets, for which international collaboration is essential. Its unique challenge, however, is that the market the foreign company is entering is completely new to it in many aspects. Merger and acquisition (M&A) are processes Continue reading
Strategic Management
Strategic management is the art and science of formulating, implementing and evaluating cross-functional decisions that will enable an organization to achieve its objectives. It involves the systematic identification of specifying the firm’s objectives, nurturing policies and strategies to achieve these objectives, and acquiring and making available these resources to implement the policies and strategies to achieve the firm’s objectives. Strategic management, therefore, integrates the activities of the various functional sectors of a business, such as marketing, sales, production etc. , to achieve organizational goals. It is generally the highest level of managerial activity, usually initiate by the board of directors and executed by the firm’s Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and executive team.
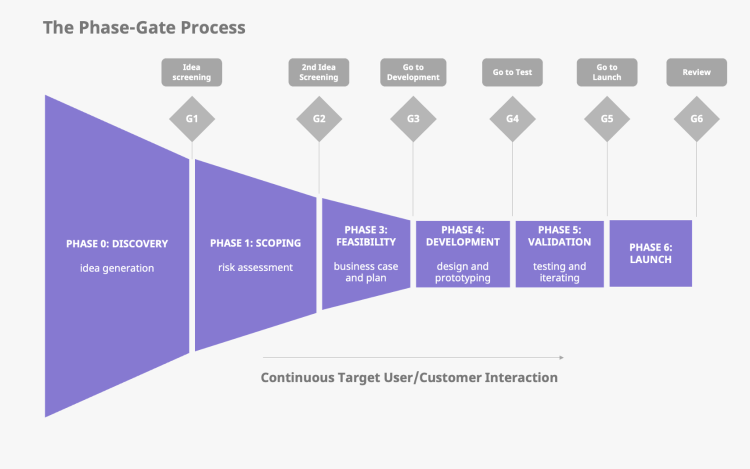
Cooper’s Stage Gate Model in Product Development
Cooper’s Stage Gate process focuses on innovations during project management/product development. The stage gate process, a notable project management technique pioneered by Dr. Robert G. Cooper in the early ’80s, systematically breaks down a project into distinct, manageable stages, punctuated by decision points known as gates. At these gates, the project’s progress is critically evaluated against predefined benchmarks, determining whether the project should progress, be adjusted, or discontinued. Entrepreneurs use a set of approaches and tools to assess the viability and potential of ideas and profit from them by developing and launching products. Cooper’s stage gate process model is one such approach that is key to any product or service in the commercial or non-commercial sector. Cooper’s stage gate process model is critical to the processes and performance of an organization as it reduces production errors and therefore saves the company from losses. This technique divides a project into different Continue reading
Free Cash Flow Theory of Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A)
In the late 1980s, Jensen (1987) introduced the free cash flow theory to explain the financial decisions of managers in investing surplus money (excess cash flow). The free cash flow theory stems from the availability of corporate funds, after the deduction of all expenses. Managers often use this fund for purposes of expanding their businesses or paying out dividends to their shareholders. However, studies shows that many managers prefer to use this excess cash to enter into merger and acquisition agreements. Their incentive may be higher profitability and business advantages that mergers and acquisitions offer (compared to other investments). Occasionally, despite the failure of some investments to increase shareholder value, managers may decide to use these funds to expand businesses (through these mergers and acquisitions). They often prefer this option because the second alternative of paying out dividends to shareholders leads to the loss of financial resources and managerial power. Continue reading
Strategic Planning Tools – SPACE, GRAND, and QSP Matrices
Strategic planning is an integral part of a successful company’s operations and processes. It allows organizations to assess their positions within industries and define the steps necessary to solve issues or rise to a higher level. Strategic planning may be performed using different tools, including SPACE, Grand, and QSP matrices. While all three are effective and helpful, the last one is implemented during the final stage of strategic planning. 1. SPACE Matrix Overall, the SPACE matrix is a specific strategic management tool that companies use to analyze their positions. SPACE stands for the Strategic Position and Action Evaluation, focusing on strategy formulation and especially the improvement of competitiveness. It has four quadrants, each defining the specific temperament of the strategy to choose: competitive, defensive, conservative, and aggressive. Further, the Y-axis top is financial strength, and the bottom is environmental stability, being the factors of the external environment. The right of Continue reading
Growth and Success of an Enterprise – Factors and Stages
There exists several factors which contribute to the growth and success of an enterprise and among the leading factors is the age of the firm. To explain why smaller and younger firms are likely to grow faster than old and large enterprises is explained in economics by the use of the concavity of the production function. Where at the start, the small capital invested has the capability of multiplying exponentially but as time moves on and new investments are injected in to the investment, the marginal rate of productivity of the invested capital declines and that explains the reason why young firms grow faster than old and already established enterprises. Although many experts indicate that as the firm ages the likelihood of it learning form its mistakes and thus succeeding are high, the multiplier effect of large business is low and this is a major contributor to the success of an Continue reading
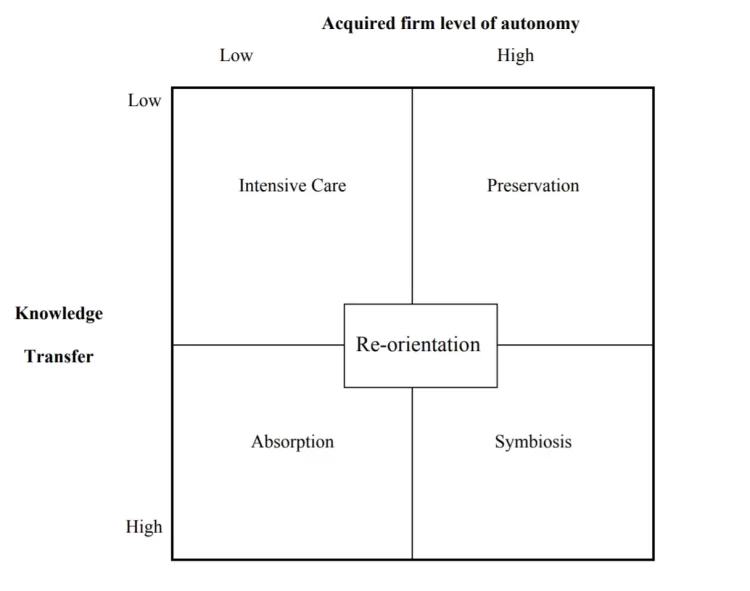
Major Theories of Mergers and Acquisitions
Nowadays, the business world is looking for continuous expansion to generate higher revenues and enhancing the quality of the production processes. Additionally, mergers and acquisitions contribute to the strengthening of the competences and stimulation of the core competitive advantage while facing the increasing and intense competition in the world. Nonetheless, the significant differences between mergers and acquisitions tend to exist due to the different nature of the phenomenon. The takeover and acquisition imply having control of the acquired firm’s equity by 50 %. In turn, the merger implies the creation of the new business unit. Despite having slightly dissimilar nature, the intentions remain the same, as they remain an essential instrument to stay competitive on the market. In turn, the concept of the synergy enhancement also has to be taking into account while improving the quality of acquisitions and justifying their importance. It is commonly known that one of the Continue reading