Change management can be characterized as the procedure of altering or changing one or more angles of an association utilizing a planned system. Change management includes the implementation of one or more techniques, which organizations use to increment effectiveness and acquire their objectives. Theorists have provided different concepts of change management simply to understand the framework according to which organizations manage and lead change. The Prosci ADKAR model is one of the best approaches introduced several years ago to support change in companies through the prism of its five major elements, namely awareness, desire, knowledge, ability, and reinforcement. The progress of the ADKAR model is evident today due to its evident advantages and the possibility to facilitate working processes. Prosci’s ADKAR Model of Change Management Prosci’s ADKAR Model is a goal-oriented change management model that guides individual and organizational change. Created by Prosci founder Jeff Hiatt, ADKAR is an acronym Continue reading
Strategic Management
Strategic management is the art and science of formulating, implementing and evaluating cross-functional decisions that will enable an organization to achieve its objectives. It involves the systematic identification of specifying the firm’s objectives, nurturing policies and strategies to achieve these objectives, and acquiring and making available these resources to implement the policies and strategies to achieve the firm’s objectives. Strategic management, therefore, integrates the activities of the various functional sectors of a business, such as marketing, sales, production etc. , to achieve organizational goals. It is generally the highest level of managerial activity, usually initiate by the board of directors and executed by the firm’s Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and executive team.
Strategy Development and Leveraging Core Competencies
Strategy allows an organisation to deliver its vision. To develop a deliberate strategy which could potentially increase the sustainability of an organisation clearly requires the identification of core competencies but often a single strategy is not the answer. Organisations require a headline strategy to fit a brief which resonates the vision but several strategies are required over many departments such as research and development, production and marketing to deliver the main strategy. The process of strategy development is complex and methodology depends on several factors including the availability of resources and the external environment. The second step in strategy development following identification of core competencies, which is the process of leveraging resources so they can be exploited for maximum benefit. An organisation’s resources can be tangible, intangible or human and that these can be matched to its capabilities to eventually provide competitive advantage. This process of exploiting the unique combination Continue reading
Transferring Core Competencies for Organization Success
Development and expansion organizations’ core competency is one of the main success factors of many organizations. However, if organizations do not apply correct measures when transferring core competencies for one business to another, the likelihood of failure is high. Transfer of core competencies is one of the most important business diversification strategies of ensuring organizations reduce costs of starting over again in new business ventures. Transferring core competencies and resource strengths from one country market to another is a good way for companies to develop broader or deeper competencies and competitive capabilities that can become a strong basis for sustainable competitive advantage. It mostly works via capitalizing on operational relatedness, primarily applying the constrained multi-product strategy. This strategy offers organizations a chance of realizing and exploiting economies of scope, a crucial pathway for gaining a competitive advantage over other businesses. In addition, it guarantees organizations opportunities for utilizing existing expertise Continue reading
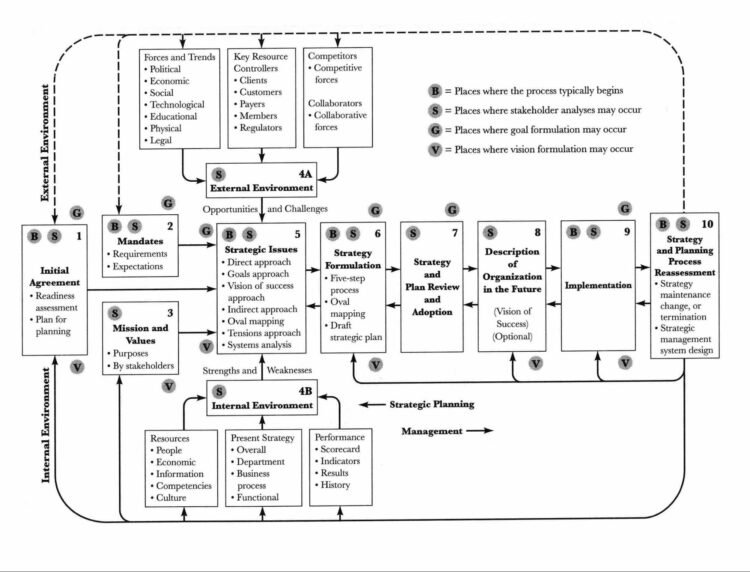
Strategic Management Model: Bryson’s Strategy Change Cycle for Strategic Planning
In ensuring effective strategic change in an organization, strategic planning is inevitable for organizations to develop and implement strategies through the strategy change cycle. A strategic change cycle is a systematic procedure that is indispensable in determining whether an organization will be successful. The strategy change cycle is among the primary processes of strategic management that links the processes of planning and implementation and ensures that the process is carried out consistently and in alignment with specific organizational goals. The following section discusses ten vertical steps in the change cycle by keenly describing why they are essential for organizations in planning and implementing their strategies. Its purpose is to develop a consistent commitment to the mission and vision of an organization, both internally and externally, at the same time with maintaining a clear focus on the organizational agenda with the help of relevant activities and decision-making processes. Strategy Change Cycle Continue reading
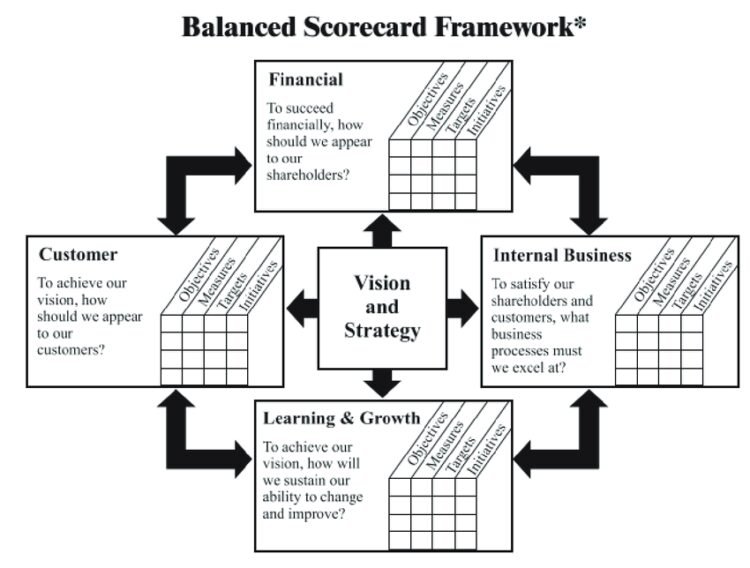
General Issues of Balanced Scorecard (BSC) Implementation in Organizations
For modern organizations, it is essential to have methods for collecting data and making decisions based on the strategic objectives that lead to the achievement of competitive advantage. The balanced scorecard (BSC) represents strategic planning and management that companies use for communicating their intended accomplishments, aligning everyday procedures with the formulates strategy, monitoring progress, and prioritizing projects. In general, BSC is used for measuring and providing feedback to organizations, with data collection being crucial to the provision of quantitative results. This data is interpreted by managers and executives who make further decisions for an organization. The concept of Balanced Scorecard (BSC) was first introduced by Kaplan and Norton who received great praise for their research. The key principle behind the concept lies in finding balance across all functions of an organization since the majority of companies focus on financial measures such as growth and profitability, forgetting about such sectors as Continue reading
Business Strategy Implementation
The business strategy will be implemented through the concerted actions of all staff working within a partnership framework. The Board will set objectives and parameters, for the business strategy implementation, and will review progress in achieving objectives. Management will take ownership, give leadership and agree with staff clearly defined roles and responsibilities in achieving targets and milestones. It is also recognized that resources issues may affect the full implementation of the strategy. To assist management in carrying out its role in delivering the strategy and whatever may evolve in the future, an integrated management development programme, with a particular focus on business planning and performance management, will a particular focus on business planning and performance management, will be provided. It is anticipated that other issues will emerge as the process evolves. The project groups will comprise of management and staff, at all levels, who have expressed an interest, and who Continue reading