The government has a responsibility for delivering public goods optimally for the collective development of all individuals. In the quest to achieve this noble course, supply side policies, which form part of macroeconomic strategies, are developed to ensure that markets and industries function in an efficient way to increase the rate of economic growth as reflected in the real national yield. Many governments support the assertion that they can achieve a sustained economic growth by improving supply side operations without causing an increase in inflation. However, reforms on the supply side policies do not facilitate the achievement of adequate growth.
Definition and Explanation of Balanced Economic Growth
Although the growth rate does not reflect people’s living standards entirely, economic growth has been one of the critical areas of consideration for every nation that is in the process of developing its economic policies. Indeed, economic growth is the most common approach to measuring the level of prosperity. Considering the drawbacks of economic growth as a measure of performance for economies such as failing to record productivity in the black markets, all nations endeavor to ensure a balanced economic growth.
In business, an objective fiscal development is realized where investment supplies and yield grow at corresponding rates. Consistent with this assertion, for overall economic growth to occur, the capital-output ratio, the real interest rate, and the labor share of income have to remain broadly constant over time. The field of development economics considers a balanced economic growth an instantaneous and synchronized expansion process of various industrial sectors within a nation. This claim presents a balanced economic growth as a maintainable financial development.
A balanced economic growth is characterized by low inflation. Consistent with the development economics point of view, a balanced economic growth occurs in different sectors of an economic. Such sectors grow simultaneously. For example, a balanced economic growth may be witnessed when exportation and domestic consumption rates rise simultaneously. It also requires a balanced growth in a nation’s markets in different regions. For instance, China’s fast expansion is mainly concentrated on the country’s southern region.
Nations that experience a balanced economic growth have no one area of the economy growing at the expense of the other. Consequently, it is necessary for investments to develop as the consumption capacity increases. This situation ensures that the witnessed increased productivity from higher investments can lead to a greater absorption of products in the local markets. For instance, the US and the UK financial intensification agenda, which centers on the increased customer expenditure, has not only resulted in a reduced funds ratio but also amplified current bank arrears.
A balanced economic growth pays attention to issues of sustainability. For instance, it considers the impacts of economic activities on the environment. Hence, a balanced economic growth utilizes non-renewable and renewable energies to drive development. An arising question is whether any nation has ever experienced a balanced financial growth. For instance, economists held a popular opinion that the UK’s economic growth was balanced from 1993 to 2007. During this period, the nation experienced a low inflation rate that was accompanied by the economic expansion in different sectors. However, the global financial crisis of 2007 proved this popular opinion wrong. Amid the low inflation levels, the economy experienced a boom of the bank-lending sector. This situation led to credit intensification.
Definition and Explanation of Supply Side Policies
Alternatively referred as Reaganomics, the principles of supply-side economics rest on the economic thinking of President Ronald Reagan, the 40th president of the United States of America. Despite him being highly controversial, the president popularized the idea that high taxation cuts offered investment and savings enticement. The enticement produced a trickling effect in the form of benefits to the entire economy.
Like any other economic theory, supply-side money matters attempt to explain the macroeconomics phenomena. The goal is to offer an alternative mechanism for ensuring stability in the economic growth. The theory is advanced in the context of three pillars, namely ruling, financial policy, and taxation guidelines. The three pillars are linked to one idea, which states that the supply of services and commodities (production) constitutes the main driver of economic development within a nation. The subject of supply-side economics operates in direct contrast with Keynesian theory, which holds that consumers drive economic expansion through their demand for commodities and services. The supply-side theory holds that producers establish the process of economic growth via their enthusiasm and the actual production of goods and services. An increase in supply results in improved productivity and lower commodity charges. The supply-side theory claims that demand is irrelevant since the process of underproduction or overproduction is unsustainable in an economy. Over-production leads to inventory accumulation, which forces suppliers to lower prices to offset the surplus.
Monetary policies imply the capacity of federal banks to elevate or lower the amount of dollars that are in circulation. A high amount of dollars in circulation means that people have a greater purchasing power. This situation creates liquidity. The three pillars of supply-side theory establish various economic policies. The policies include privatization, deregulation, lessening of the revenue duty, the rising of shares in the education and training processes, a decline of supremacy that is vested in trade unions, pecuniary market deregulation, the establishment of few duty barriers, enhancement of transportation and infrastructure, and labor bazaar deregulation among others.
According to supply siders such as the EU, the labor bazaar deregulation raises competitiveness by ensuring ease of firing and/or recruiting human resources. The supply-side theory asserts that market failures create the necessity of the government to intervene in terms of improving infrastructure with the objective of lowering a firm’s costs. The theory encourages the deregulation of nations’ financial markets to permit more competition so that people can borrow money at discounted costs.
How Supply Side Policies Bring about a Balanced Economic Growth?
A balanced economic growth occurs when the economy develops in all sectors and regions. It is also important for a nation to experience low inflation levels for such growth to be possible. Supply-side policies lower inflation by shifting the AS (Aggregate Supply Line) towards the right. This change causes the reduction of prices. By ensuring that the economy runs efficiently, the policies lead to a decline in costs. The decline influences inflation. For a balanced economic growth to occur, the level of employment should grow consistently with the production levels.
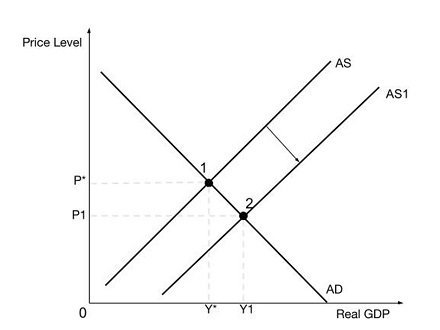 Supply-side policies reduce structural and fractional challenges that lead to unemployment. It also lowers the real wage unemployment so that joblessness goes down naturally. By increasing the AS, supply-side policies ensure sustainability in a nation’s economic growth. Sustainability is a necessary condition for balanced economic growth. The policies boost the productivity of nations by increasing their ability to export so that their competitive advantage increases. Since they also increase the rate of employment, people have more financial resources, which increase their buying power. Consequently, supply-side policies not only increase domestic consumption but also widen the export bazaar.
Supply-side policies reduce structural and fractional challenges that lead to unemployment. It also lowers the real wage unemployment so that joblessness goes down naturally. By increasing the AS, supply-side policies ensure sustainability in a nation’s economic growth. Sustainability is a necessary condition for balanced economic growth. The policies boost the productivity of nations by increasing their ability to export so that their competitive advantage increases. Since they also increase the rate of employment, people have more financial resources, which increase their buying power. Consequently, supply-side policies not only increase domestic consumption but also widen the export bazaar.
Maintaining low tariff barriers raises trade while a decline in welfare benefits encourages unemployed people to seek jobs to increase a nation’s production capacity. Through the privatization of supply-side policies, people can acquire quality services at a competitive cost. Supply-side economists claim that tax reduction increases the amount of money that is available to investors for use in production activities to increase their production levels and employment demands.
Therefore, the increasing number of people who are taxed small amounts compensate for reduced revenues. However, as revealed in the section on the effectiveness of supply-side policies in ensuring a balanced economic growth, the policies have been subjected to criticism by various economists based on their theoretical and practical application.
Effectiveness of Supply Side Policies in Ensuring a Balanced Economic Growth
President Reagan applied supply-side policies with the objective of ensuring a balanced economic growth in the US. The president described the problem of inflation as a condition that was initiated by too many dollars, which could only help in buying very few goods. Paul Volcker, the then chairperson of the Federal Reserve, dropped the monetarist policy to focus on increasing the control of monetary economic policies. However, critics reckon that Reaganomics were ineffective in decreasing tax revenues at a constant dollar. To this extent, supply-side economics argument that a reduction of taxation raises revenues was challenged.
President Bush also deployed supply-side policies to induce a balanced economic growth. However, his taxation cut failed to guarantee economic expansion since various macroeconomic growth indicators fell below the industry average during the 2001 to 2005 cycle. The supply-side policies of President Bush only reduced the government’s revenues while raising deficits. The situation interfered with the equality of after-tax incomes. However, President Bush indicated that the US economy would experience sustainable and long-term growth in terms of GDP and employment levels, which would in turn increase individual and household incomes while at the same time reducing the government’s deficits. Instead, the global financial crisis of 2007 produced converse effects. The experience was another proof of the ineffectiveness of supply-side economic policies in ensuring a balanced economic growth.
Nations can address their joblessness issues effectively through supply-side strategies. For example, one of the supply-side policies entails investing in education and training, especially for unemployed youths. Such people can acquire knowledge and skills, which boost their employability chances. However, focusing on schooling and tuition may consume many years before producing significant results on financial expansion. No guarantee is given that supply-side economic policies such as training can reduce unemployment levels. For example, some people may not take the training opportunities. A policy such as deregulation on the hiring and firing of employees may create unpredictable temporary unemployment within a nation.
In the process of fighting against inflation, it is more effective to deploy strategies such as monetary policies. The can also control and monitor AD (Aggregate Demand) via scheming the interest rates. Supply-side policies take a long time to deal with the pressures of inflation. Consistent with the supply-side theory, increasing productivity is useful in ensuring a balance of payments. When organisations compete, goods that are produced within a nation have a higher demand.
To sum up, the balanced growth concept underscores the importance of ensuring that the various components of the GDP grow at an equal rate. By fostering balanced growth, economies are in a position to promote equitable economic development across the different regions. Subsequently, the probability of attaining equitable distribution of wealth is increased substantially. Governments can adopt different approaches in order to achieve balanced growth. One of these approaches entails the formulation of effective supply side policies, which entail the attempts undertaken by governments in an effort to stimulate productivity, hence the economy’s productive capacity. By implementing the supply side policies, governments are in a position to promote the establishment of a flexible labor market. Governments have the option of implementing two main categories of supply side policies, viz. the interventionist and market-based policies. The interventionist policies emphasize on protecting the occurrence of a market failure, for example by providing public goods. Examples of such policies entail investing in human capital training, technology development, and the formulation of regional policies in order to promote equitable economic growth. Furthermore, interventionist policies also involve enacting reforms in the labor market and the provision of tax incentives such as tax cuts.