Accounting fraud is the manipulation of financial statements in order to benefit the business financially or to create a false appearance of financial health. In the situation of Caterpillar Inc. (CAT) – a manufacturer of heavy construction and mining equipment, diesel-electric locomotives, diesel, and natural gas engines, and industrial gas turbines – the payment of federal income taxes on their earnings was avoided to boost the company’s financial status, saving the company billions of dollars and keeping its stock price high. CAT, having more than 500 locations worldwide – including the Americas, Asia Pacific, Europe, Africa, and the Middle East – is vast in size and an economic standpoint, with sales and revenues of $53.9 billion in the year 2019. However, a lawsuit against Caterpillar Inc. for inadequate tax disclosure had greatly impacted the company from the time period of 2013 to 2017. A great portion of Caterpillar Inc.’s investigation Continue reading
Business Ethics
Ethical Issues in Human Resource Management
Business ethics are the moral doctrines that direct the way to business behave. Business ethics determines the actions of every individual that distinguish the right or wrong. Every business organization must develop the codes of conduct and ethics that should be followed by all the members. Ethics can be taken as the crucial way to self-presentation and public perception of the organization. Ethics in human resource management is related to the employee’s issues. Human resource management plays an important role in setting up and implementing ethics in the workplace. Implementation of ethics in the workplace has been one of the challenging tasks for the organization. Various human resources issues can be handled properly by the application of ethics and code of practices by the managers in the workplace. Ethics generally determine what is right and what is wrong. With the help of business ethics, proper allocation and maintenance of employee Continue reading
Case Study on Business Ethics: McKinsey Opioid Scandal
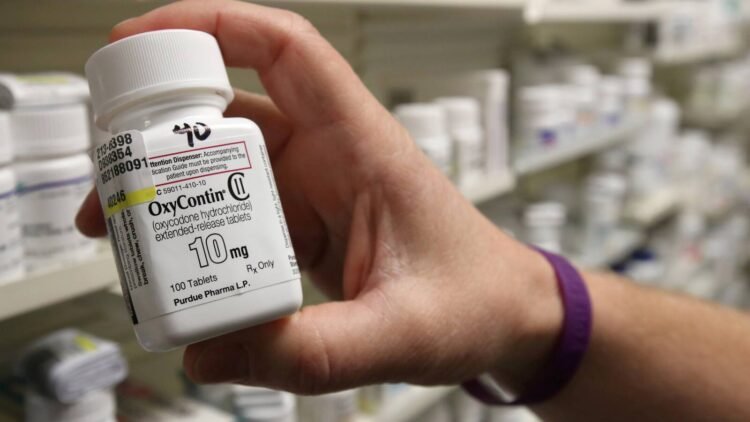
McKinsey and Company, a leading consulting agency, has agreed to pay US$573 as a settlement for advising Purdue Pharma, a drug company, on how to “supercharge” opioid sales. The agreement to pay the settlement was reached after the management of the consultation firm agreed with attorney generals of 47 states, Massachusetts court records revealed. This action disrespects human rights, especially for the patients of the drug produced by Purdue Pharma. The decision to settle was made in February 2021 when the Company’s unethical advice to the pharmaceutical organization was disclosed. For about a decade, McKinsey advised Purdue on ways to brand and market opioids and influence doctors into prescribing high doses of opioids. The consulting firm also ensured that Purdue maximized its profits by offering guidance on evading pharmaceutical prescriptions. In addition, McKinsey was also known to be involved with other opioid-related works, including consulting advice to Johnson & Johnson, Continue reading
Case Study on Business Ethics: The Wells Fargo Fake Accounts Scandal
Wells Fargo, one of the largest and most profitable banks in America, struggles to repair its dented image after it was caught in a mega fraudulent accounts scandal. The San Francisco-based bank had its management pressure on its employees to meet unrealistic sales targets, which led to the fake account incident. The customers were forced to pay bank charges they did not know about, and it was much later that the scandal was unraveled. Between 2011 and 2015, more than 1.5 million accounts were opened by Wells Fargo employees, and 565,000 credit cards were applied in customer’s names without their authorization. During a lawsuit by the government regulatory bodies, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), the Department of Justice (DOJ), and the Federal Reserve, it was established that Wells Fargo blatantly falsified its bank records. Apart from the hefty fines that have been imposed on Wells Fargo, there are lessons Continue reading
Earnings Management – Definitions, Reasons and Examples
Earnings Management (EM) is the term used to describe the process of manipulating earnings of the firm to meet management’s predetermined target. The flexibility of accounting standards may cause some variability in earnings to occur as a result of the accounting choices made by management. However, earnings management that falls outside the generally accepted accounting choice boundaries is clearly unethical. The intent behind the earnings management also contributes to the questionable ethics of the practice. Some managers use EM as a means of deceiving shareholders or other stakeholders of the organization, such as creating the appearance of higher earnings to increase compensation or to avoid default on a debt covenant. The intent to use EM to deceive stakeholders implies that it can be unethical, even if the earnings management remains within the boundaries of GAAP or IAS. Earnings management has been defined as management’s exploitation of accounting flexibility to meet Continue reading
Case Study on Corporate Governance: WorldCom Scandal
Established in 1988, WorldCom was formed so that the strongest, most capable public relations firms could serve national and international clients, while retaining flexibility and client- service focus inherent in independent agencies. Through WorldCom, clients have on demand access to in-depth communication expertise from professionals who understand the language, culture and customs in the geographic areas of operation. WorldCom has 105 offices in 90 cities and 40 countries on five continents, more than 2000 employees and recorded revenue of US $ 243.5 million in 2008. In the 90’s WorldCom was involved in acquisitions and purchased over 60 firms. The complete financial integration of the acquired company must be accomplished, including an accounting of assets, debts, and a host of other financially important factors. WorldCom moved into Internet Traffic, controlling 50% of US Internet Traffic and 50% of the e-mails worldwide. In 1997, WorldCom and MCI completed a US $37 billion Continue reading