Public good refer to a commodity whose utilization is determined by the society and not an individual and financed by means of taxation. In contrast, an International public good can be defined as a utility that provides specifically well-defined benefits to everyone across the globe. An international public good does not imply that benefits are available to every person in every country but means that they are available to the global public per se. The effectiveness of public goods depends on two core factors: individuals’ preferences or taste, and capability for consumption. For example, uneducated individuals cannot benefit from global knowledge because of their inability to read and comprehend knowledge material. The Economic Concept of Public Goods A public good can be defined on economic basis as a utility that everybody enjoys in union with others in the sense that the consumption of that good by an individual does not Continue reading
Economics Basics
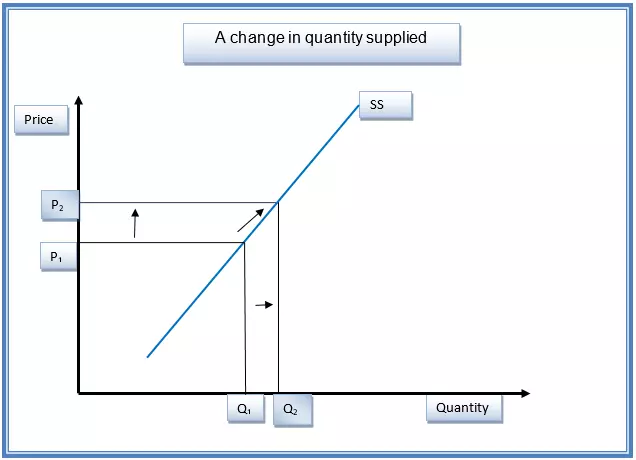
Change in Quantity Supplied Vs. Change in Supply
There is a difference between a change in supply and a change in quantity supplied. The differences are explained below. A Change in Quantity Supplied Change in quantity supplied can be explained as the movement long a stationary supply curve while holding other factors constant. This movement is drawn from the law of supply, which states that there is a positive relationship between price and supply while holding other factors constant. Thus, if the price moves up along the y-axis, the quantity supplied will move to the right along the x-axis. A change in quantity supplied is caused by price movements. This relationship is shown in the graph below. An increase in price from P1 to P2 will cause an upward movement on the supply curve, as shown by the arrow. This will cause the quantity supplied to increase from Q1 to Q2. Change in Supply Change in supply is Continue reading
Cross Price Elasticity of Demand Explained
When it comes to Cross-elasticity of demand, we must first illustrate the concept of elasticity of demand. We can say that elasticity of demand is the foundation of the theory of cross-elasticity of demand because elasticity of demand is related to only one good while cross-elasticity of demand is about the relation of two goods. We should first compare the elasticity of demand with the cross-elasticity of demand. Elasticity of demand is sometimes referred to as the own-price elasticity of demand for a good, such as the elasticity of demand with respect to the good’s own price. Elastic demand reflects that consumers are very price sensitive. This concept is understandable because we all know price is one of important determinant of quantity, and the quantity demanded of a good is negatively related to its price. We can suppose: for a seller, lower price promotes sales; for a buyer, higher price constraints Continue reading
Major Sources of Internal Economies of Scale
In business today, some companies enjoy the Economies of Scale while others do not. The difference between the companies that enjoy economies of scale and those that do not is based on the volume of output. Companies that are involved in large scale production are more likely to enjoy economies of scale compared to those that specialize in small scale production. Having understood the basic principle of the economies of scale, it becomes easier to define it. Economies of Scale is defined as the cost advantage caused by the volume of large scale production. It is the reduction of cost-per-unit as a result of large scale production. There are two categories of Economies of Scale, external and internal. Internal Economies of Scale include Technical, Financial, Commercial, Managerial and Risk Bearing among other factors. Major sources of internal Economies of Scale are discussed below. 1. Technical Economies of Scale With the Continue reading
Ricardo’s Labor Theory of Value
Ricardo’s theory of value focuses on determining the exchange value of a commodity by evaluating the current and past labour employed in the production of the commodity. The theory determines the past labor by analyzing the cost of capital, which entails aspects such as the value of tools, equipment, implements, and buildings involved in creating a commodity while the current labor entails the quantity of skills input in the production of raw materials. For example, changes in the exchange rate of a beaver for a deer over time to a tune of one beaver for five deer would mean that the labor input in catching a beaver has increased significantly compared to the labor invested in harvesting a deer. Ricardo’s theory shifts away from the analysis of the fair and equitable value (price) of a commodity to the determination of the quantity of a good or service that the commodity Continue reading
Concepts of Public Goods, Externalities, and Government Intervention
The competitive of the marketplace is very beneficial to the public in that it ensures that the very scarce resources are made available to the public in their highest values. Despite this benefit, there are certain limits to the marketplace. For instance, the production of a certain good that is economically important to both consumers and producers or even to the nation may be prohibited. In other cases, their production may either be below or above the average or required production. This situation is referred to as market failure which occurs when the marketplace fails in its allocation of resources meant for production of goods by either under allocating or over allocating the resources. When such cases occur, the government, then, comes in to play its economic role to the public. This is because the marketplace is considered a private sector of the economy rather than a public venture. However, the Continue reading