A market economy can be defined as an economy in which the allocation of resources is determined only by their supply and the demand for them. Market economy can also be defined as an economic system in which economic decisions and the pricing of goods and services are guided solely by the aggregate interactions of a country’s citizens and businesses and there is little government intervention or central planning. To conclude, the market economic system is basically a system whereby private individuals take up the responsibility of allocating resources to the public and relies chiefly on market forces to determine prices. Countries practicing the market economic system tend to assume that the forces of demand and supply are the main determinants of what is right for a nation’s well-being. They {the countries} rarely experience government interventions such as price fixing, license quotas and industry subsidizations. In reality, the market economy Continue reading
Economics Basics
Comparison of Different Economic Systems
Any system that involves the mechanism for production, distribution and exchange of goods apart from consumption of the goods and services within the different entities can be classified as an Economic System. The various kinds of economic systems and their classifications broadly follow the methods by which means of ownership are established. Thus, the mode of ownership of capital leads to the different kinds of economic systems in vogue. This article focuses on three types of economic systems, such as market, command, and mixed economy. It compares and contrasts these types in terms of the role of the government in their functioning, property and land ownership, mechanisms of price formation, division of labor, and income distribution. Market Economy vs. Command Economy A market economy can be described as an economic system where the production means are largely privately owned and aimed at profit and the process of capital accumulation. In Continue reading
The Concept of Profit Standards in Managerial Economics
Standards of reasonable profits are determined when a firm chooses to make only reasonable profits rather than to maximize its profit. The questions that arise in this regard are as follows: What form of profit standards should be used? How should reasonable profits be determined? These questions can be understood after going through the following explanatory points. Forms of Profit Standards Profit standards is determined in terms of the following: Aggregate money terms Percentage of sales, and Percentage return on investment. All these standards are determined for each product separately. Among all the forms of profit standards, the total net profit of the firm is more common than other standards. But when the purpose is to discourage the competitors, then the target rate of return on investment is the appropriate profit standard, provided the cost curves of competitors’ are similar. The profit standard in terms of ratio to sales is Continue reading
Unemployment – Meaning, Causes and Effects
The economists describe unemployment as a condition of jobless within an economy. Unemployment is lack of utilization of resources and it eats up the production of the economy. It can be concluded that unemployment is inversely related to productivity of the economy. Unemployment generally defined as the number of persons (It is the percentage of labor force depends on the population of the country) who are willing to work for the current wage rates in society but not employed currently. Unemployment reduces the long run growth potential of the economy. When the situation arises where there are more other resources for the production and no man power leads to wastage of economic resources and lost output of goods and services and this has a great impact on government expenditure directly. High unemployment causes less consumption of goods and services and less tax payments results in higher government borrowing requirements. The Continue reading
4 Important Types of Decentralization
The term “decentralization” embraces a variety of concepts which must be carefully analyzed in any particular country before determining if projects or programs should support reorganization of financial, administrative, or service delivery systems. Decentralization—the transfer of authority and responsibility for public functions from the central government to subordinate or quasi-independent government organizations and/or the private sector—is a complex multifaceted concept. Different types of decentralization should be distinguished because they have different characteristics, policy implications, and conditions for success. Types of decentralization include political, administrative, fiscal, and market decentralization. Drawing distinctions between these various concepts is useful for highlighting the many dimensions to successful decentralization and the need for coordination among them. Nevertheless, there is clearly overlap in defining any of these terms and the precise definitions are not as important as the need for a comprehensive approach. Political, administrative, fiscal and market decentralization can also appear in different forms and Continue reading
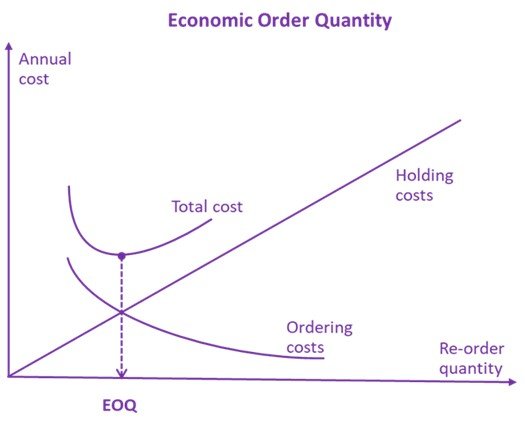
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) – Definition and Formula
In today’s marketplace, optimization of resources, their adequate use, and cost reduction are the key attributes of a successfully developing company capable of competing effectively. For the qualitative analysis of available resources and the possibility of their optimal use in business practice, there is a large number of methods and models used depending on specific tasks. One of them is Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), which is a model used to determine the optimal quantity of goods or materials to be ordered at a given time in order to minimize the total cost of inventory. The point of minimizing inventory is to save costs since unsold goods take up space, to reduce risks since inventories can become obsolete or physically obsolete, which is especially true in the food industry, and to increase efficiency since excessive inventory can make it difficult to account for them. Thus, EOQ seeks to eliminate situations in Continue reading