Poverty – A Multidimensional Phenomenon Poverty has many faces, and multiple indicators are used to capture the different deprivations experienced by a population. This complex phenomenon is linked to economic wellbeing, capability, and social exclusion. Poverty is a major moral problem because of the suffering it causes and the disadvantages conferred to some population segments. It is defined as a persistent and debilitating social condition attributed to diverse causes that affect a person’s physical, mental, and emotional wellbeing. The complex nature of poverty means that multiple measures are used depending on a country’s priorities. 1. Economic Wellbeing Income and consumption are key quantifiable indicators of poverty in society. These variables measure economic wellbeing and contain absolute, relative, and subjective components. At the basic level is absolute poverty, which describes the lack of necessities needed for survival – shelter, clean water, and food. Here, the quality of survival is an important Continue reading
Economics Basics
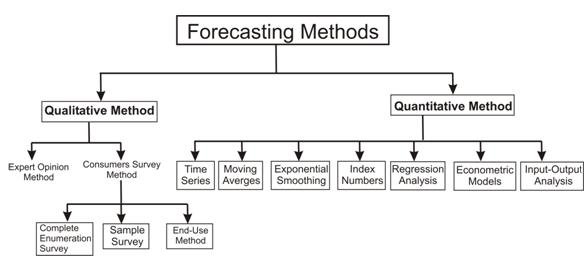
Expert Opinion Method of Demand Forecasting
In this method of demand forecasting, the firm makes an effort to obtain the opinion of experts who have long standing experience in the field of enquiry related to the product under consideration. If the forecast is based on the opinion of several experts then the approach is called forecasting through the use of panel consensus. Although the panel consensus method usually results in forecasts that embody the collective wisdom of consulted experts, it may be at times unfavorably affected by the force of personality of one or few key individuals. To counter this disadvantage of panel consensus, another approach is developed called the Delphi method. In this method a panel of experts is individually presented a series of questions pertaining to the forecasting problem. Responses acquired from the experts are analyzed by an independent party that will provide the feedback to the panel members. Based on the responses of Continue reading
Different Approaches to Profit in Managerial Economics
Profit is the reward which goes to organization as a factor of production for its participation in the process of production. Profits differ from other factor rewards in the following ways: Profit is a residual income left after the payment of contractual rewards to other factors of production. The entrepreneur while hiring other factors of production enters into contract with them. He pays wages to workers, rent for land and interest for borrowed capital and the residue or whatever is left is his profit. Thus profits become non-contractual in character. The various factors of production are rewarded even before the sale of the product and irrespective of its sales whereas profits accrue only after the product is sold. The rewards of other factors have been fixed. They do not fluctuate whereas profits go on fluctuating so much so that the entrepreneur bears the risk of even incurring losses which we Continue reading
Special Pricing Approaches Used in Business
A variety of approaches are employed by businessmen in setting prices. These approaches are not mutually exclusive but sometimes they complement or supplement one another. Some of them are: Intuitive Pricing: It is a psychological method of pricing in which prices are based on the ‘feel of the market’. The system is more subjective rather than objective in nature. Initially the price is estimated on the basis of cost plus method with flexible mark-up pricing. This method is fairly common. Experimental Pricing: It is a trial and error method of pricing. This method is widely used in pricing of new products especially at retail level. Initiative Pricing: In this method a firm decides to follow a price fixing policy of a price leader. Backward Cost Pricing: Certain industries target price as the starting point for strategic calculations. The selling price is determined first and by working backwards the firm arrives Continue reading
Deficit Spending- Meaning, Advantages and Disadvantages
Deficit spending is the amount the government consumes that overtakes revenue over a particular budget year. Globally, it is a system used by most governments for economic stability. Deficit spending can be of either positive or negative impacts depending on the country’s aim in applying it. If well-strategized, it can be of immense aid to rescue the economic growth; it benefits every person in that specific government by opening room for investors. Deficit spending takes place when the government consumes more than the revenues. The government uses deficit spending for economic growth by opening opportunities for private sectors. For example, the private sector can offer loans to people so that they can start their businesses. In deficit spending, the consumption rate is higher than the profit that the government acquires. Therefore, the government spends more than what is available in addition to having more needs. Deficit spending multiplies huge debts Continue reading
What is an Economic System?
A market can be defined as a place where the forces of demand and supply operate or where buyers and sellers can interact – directly or indirectly – to trade goods and services. This therefore means that marketing is the process of identifying, anticipating and satisfying consumer requirements effectively and profitably. The concept of marketing is basically to make profit by satisfying consumers in a particular location. In conclusion, the idea of a market and the concept of marketing can be utilized as the economic system of a country/state. Economic System can be defined as a refereed journal for the analysis of causes and consequences of the significant institutional variety prevailing among all developed, developing, emerging, and transition economies. It can also be defined as an organized way in which a state or nation allocates its resources and apportions goods and services in the national community. The major function of Continue reading