Economists make a statement that there is nothing like free lunch and this is a fact. It should be known that this is a popular adage that has been used to communicate economic aspects for a long period of time. In this case, economists are just saying that it is literally impossible for an individual to get something for free without giving out anything. This means that you can not expect to get something for nothing. There has been an argument that this phrase is the core of economics which is undisputable. The whole issue of free lunch can be evaluated and looked at from different perspectives depending on the prevailing situation. For instance, we can look at this aspect from an opportunity cost point of view whereby an individual will be expected to trade off one thing for the other. This means that a decision has to be made as Continue reading
Economics Concepts
Income and Substitution Effect Explained
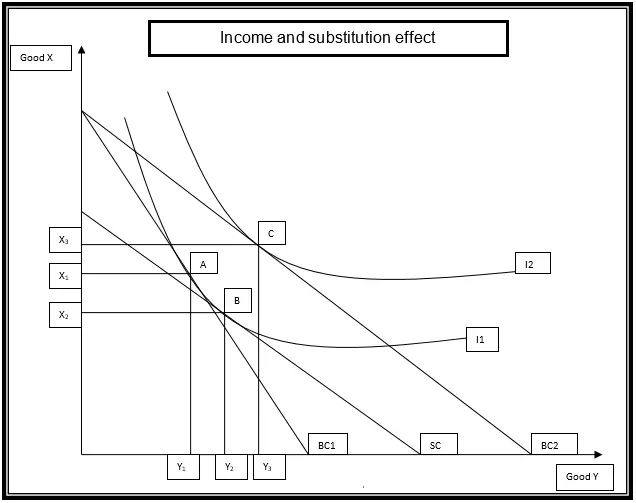
Based on the law of demand, a change in price can be described in terms of income and substitution effect. The diagram presented below will be used to explain these effects. The two items that will be analyzed are commodity Y and X. According to the law of demand, a drop in the price of commodity Y will lead to an increase in quantity demand. The increase will cause the budget line to pivot from BC1 to BC2. Also, the indifference curve will shift from I1 to I2. This represents a movement to a higher indifference curve. The equilibrium position is the point of tangency between the budget line and the indifference curve. When the price of commodity Y falls, a consumer will be indifferent between consumption at point A and B because they lie on the same indifference curve. However, at point B, the consumer shall not have exploited Continue reading
Diverse Production Modes Beyond Capitalism in Global Economy
Despite the predominance of capitalism as the mode of production in the current global economy, communism, independent production, slavery and feudalism have remained active in the production modes in the society. This analytical treatise attempts to explicitly explore the tenet of existence of other modes of production besides capitalism in the present society. Through the universal principles of intelligible strategies, governments across the globe are keen on production interventions that aim at protecting the infant companies. The governments operating on this assumption have to ensure their own survival by protecting their industries and trade policies. This action represents the communist production mode which is characterized by the need to serve self interest above the interest of the competitors. The prime principle of communism is featured by interconnected holistic phenomenon. The conscientious citizenship needs to perceive the global interrelationship since the world is marked with inclusive model of integration; the world explores several Continue reading
Marxism Perspective in Production
Karl Marx explains the concepts of production such as means, relations, and modes using the various economic systems. In the perspective of Marx, individuals engage in production because they have to fulfill a need. According to Marx, economic systems deal with the development of strategies and policies that govern the behavior and employment of the means of production. In the explanation of Marx, means of production are the initial components that determine production and facilitate efficient production processes. The basis of the argument that Marx advances is that the means of production comprise instruments of labor, for instance, machines, computers, factories, and equipment used in adding value to products. In addition, he argues that subjects of production include raw and natural resources that people manufacture, process, or design. Marx believes that when individuals devise the initial step of production, which entails arrangement of the means of production in an organized Continue reading
Trickle-Down Economics or Reaganomics
In economics and politics, the term trickle-down economics or Reaganomics is the pejorative term for the theory that taxing the wealthiest individuals in society less will in allow those individuals to invest more of their money into the economics development and create new jobs for the middle and lower class. Proponents for the theory use the term supply-side economy, considering that the idea of the middle to lower classes tangentially receiving benefits through economics policy which directly benefit the rich is somewhat insulting. The basic idea is that the recipients of the tax cuts will then be able to invest more money into infrastructure, opening more stores and companies, which will then provide more jobs as well as drive down the prices of goods. However, in terms of economic theory, there have been no major economists who have ever supported this theory or have attempted to defend the “trickle-down” aspect Continue reading
Effect of Price Controls on an Economy
A lot has been said about open economies but the fact is that their existence is only in theory. It is common knowledge that all countries in the world have some entry restrictions in their markets. With this in mind, open economies are described as those countries whose policies allow production and pricing to be determined by the forces of supply and demand. The aforementioned restrictions are, therefore, in the form of policies that countries develop in a bid to accelerate economic growth. One of such policies is price control in which a government gives price floors and/or ceilings for products, rent, wages, etc. This article is an in-depth investigation of the effect of price controls like rent control and minimum wage on the efficiency of an economy. Importance of Price Controls Price controls are a very important part of any market. They play very important roles in protection of consumers Continue reading