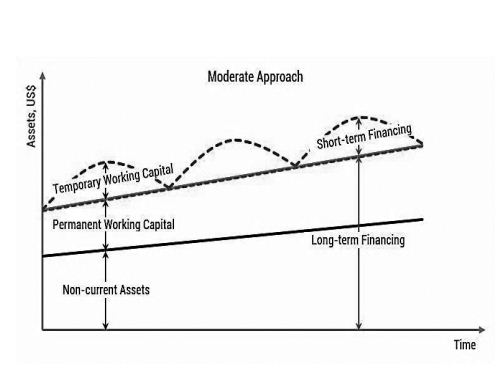
Working capital is said to be the life blood of a business. Working capital signifies funds required for day-to-day operation of the firm. In financial literature, there exist two concepts of working capital namely: gross and net. Accordingly, gross concept working capital refers to current assets viz: cash, marketable securities, inventories of raw materials, work-in-process, finished goods and receivables. According to net concept, working capital refers to the difference between current assets and current liabilities. Ordinarily, working capital can be classified into fixed or permanent and variable or fluctuating parts. The minimum level of investment in current assets regularly employed in business is called fixed or permanent working capital and the extra working capital needed to support the changing business activities is called variable or fluctuating working capital. There are broadly 3 working capital management strategies/ approaches to choose the mix of long and short-term funds for financing the net working Continue reading
Financial Management Concepts
Financial Analysis – Meaning, Definition and Methods
Financial statements are the source of information that present the economic value of a company to the external users. Several articles and books has defined the Financial analysis as to combine financial statement, financial notes, with other information, to evaluated the past, current, and future performance and financial position of company for the purpose of making investment, credit, and other economics decision. Financial Analysis is concerned with risk factors that might affect the future performance of a certain company. Financial analysis is concerned with different aspects of the company, in general financial analysis deals with profitability (ability to generate profit from delivering good and services), cash- flow generating ability (ability to generate cash inflows exceed cash outflows), liquidity (the ability to meet short term obligation), and solvency (the ability to meet long term obligation). In order to conduct a full, comprehensive analysis, analyst must collect information concerning economy, industry, competitors, Continue reading
Principles of Working Capital Management
Working capital management is concerned with the problem that arises in attempting to manage the current assets, the current liabilities and the inter-relationship that exist between them. The goal of working capital management is to manage a firm’s current assets and current liabilities in such a way that a satisfactory level of working capital is maintained. The financial manager must keep in mind the following principles of working capital management: Principle of Optimization:The level of working capital must be so kept that the rate of return on investment is optimized. In other words, the working capital should be maintained at an optimum level. This is the point at which the increase in cost due to decline in working capital is equal to the increase in the gain associated with it. According to the principle of optimization, the magnitude of working capital should be such that each rupee invested adds to Continue reading
Liquidity and Profitability Trade-Off
Differences Between Liquidity and Profitability The liquidity is the ability of a firm to pay its short term obligation for the continuous operation. A firm is considered normally financially solid and low risky which has huge cash in its balance sheet. The liquidity is not only measured by the cash balance but also by all kind of assets which can be converted to cash within one year without losing their value. It has primary importance for the survival of a firm both in short term and long term whereas the profitability has secondary important. The profitability measures the economic success of the firm irrespective to cash flow in the firm. It is often observed that a firm is very profitable in its books but it does not have sufficient cash and cash equivalent to pay its daily bills and due obligations. That is an illustration of classical poor liquidity management. Continue reading
Difference Between Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI)
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI) are the two most important terms of the market. The major difference between the two could be explained as one takes the form of investment and other financing. They are usually adopted by most developing countries. The measurement criteria for both the terms lie in the capital contribution made in the particular company or market. The most advantageous thing is the ignorance of debt creation. This is why these terms are preferred than External Commercial Borrowings which creates a debt trap for most of the countries. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) could be defined as an investment by non-residents mostly the business entities to establish business operations in a country with the proper management of equipment’s, machineries, marketing, personnel etc. In the established company the non-resident entity takes over a considerable stake to get the ownership rights and enjoys the management control Continue reading
Effects of Price Level Changes on ROI and RI
The price level changes are a common phenomenon and will introduce entirely new distortions into ROI and RI measures. The principal distortions occur because revenues and cash costs are measured at current prices, while the investment cost and depreciation charge are measured at historical prices used to acquire the assets. Depreciation based on historical cost underestimates what the depreciation charge would be based on the current cost. This results in overstating the firm’s income. At the same time, the firm’s investment is understated, because most of firm’s assets were acquired in precious years at lower price levels than those currently prevailing. The combination of overstated net income and understated investment causes the ROI or RI measures to be much higher than if inflation had not occurred. The increased ROI or RI is not a signal of higher profitability and it is mainly due to a Continue reading