Reward management entails the formulation, maintenance, communication and evaluation of reward processes that assist an organization in enhancing its performance as well as achieve its objectives. Successful organizations manage their reward practices in such a way that enables them to come up with accurate predictions with regards to what innovations are best suited for the organization as well as ensuring that whatever activities that they engaged in currently will assist them in delivering the expected results. Such organizations strive to avoid ‘folly of rewarding A while hoping for B’. These organizations opt for the evidence based management approach. Evidence-based reward management refers to the kind of management approach that is justified by improvement in the organization’s performance. In other words, it implies that the effectiveness of the reward management approach can be measured against a certain set of indicators to ascertain whether they have impacted the performance of the organization in Continue reading
HRM Functions
Achieving Sustained Competitive Advantage Through Strategic HR Management
Human resource management (HRM) is the art of managing employees in an organization. It involves the use of people to achieve organizational objectives in a productive manner and still satisfy the needs of individual employees. This is the traditional approach to human resource management. Human resource management has always been viewed as a department set apart from the rest of the organization. Lately however, the human resource department has had to justify its existence within an organization due to the increase in use of technology in place of human resources. The move is an attempt by the HR department to remain relevant to an organization in the face of the current technological changes. This has led to the emergence of Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM). SHRM is a form of management that links HRM with organizational goals and objectives to improve performance and to strengthen organizational culture. SHRM focuses on organizational Continue reading
High Performance Working (HPW) Approach to Organization Performance
Business leaders should implement powerful concepts in their organizations to meet employees’ needs and improve performance. The High Performance Working (HPW) approach is one of the concepts that can make a difference in a given organization. This approach has been embraced by managers to create and sustain High Performance Work Systems (HPWS). The Concept and Components of High Performance Working (HPW) According to the United Kingdom Commission on Employment and Skills, High Performance Working (HPW) focuses on the best strategies to manage organizations and empower employees to focus on every business objective. The implementation of the concept has been considered to maximize employee commitment, thereby delivering improved levels of performance. The model is designed in such a way that employees are guided and supported to put adequate efforts into their activities. Consequently, the workers utilize their competencies and ideas in an attempt to support the goals of the targeted organization. Continue reading
Unitarist and Pluralist Perspectives in Human Resources Management
Employee relations and management is an essential aspect of organisations. This cuts across organisations that prevailed in ancient days and the organisations in the modern days. Different models and perspectives have been adopted by various organisations to manage employees. The employee relations in organisations emerged amidst industrial relations which began in the 1920s in Europe. During this time, ‘industry’ was the term used to mean ‘the manufacturing firm’. However, in modern days, the meaning of the word has expanded to include the manufacturing firms and other sectors of the economy that do not deal with manufacturing. The definition of industrial and employee relations covers all forms and kinds of employment. Scholars in the field of industrial and work relations have come up with three management perspectives that differ significantly. These perspectives are different in their explanation, understanding and analysis of relations at places of work. These theories include the unitarist Continue reading
Case Study of Coca-Cola: Performance Management System (PMS) and Training
The growth of businesses depends on the strategic plans, goals, values, cultures, and norms implemented within a given institution. Multi-national companies like Coca-Cola have dominated the global markets for the past five decades based on adopting performance management and training principles in running activities since its inception in the beverage industry. The organization has an ongoing process of job clarification and open communications within the workspace, a decision that promotes the productivity of workers and the profitability of the firm at large. Performance management promotes coordination between managers and workers through an open-aided communication approach to achieve organizational objectives. Training employees to align with organizational strategic goals starts with clarifying job responsibilities, workplace expectations, developmental planning, and priority setting. Analyzing the strategies of planning, monitoring, developmental, rating, and rewarding employees at Coca-Cola exposes the impact of performance management systems in improving workers’ performance. The Current System in Coca-Cola Coca-Cola’s management values Continue reading
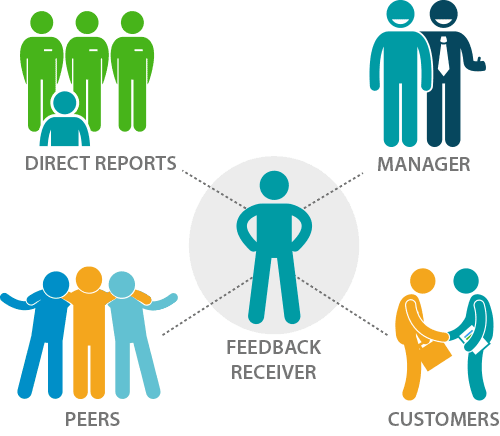
360 Degree Feedback – Meaning, Process, Pros and Cons
360 degree feedback is an assessment evaluation tool that is focused on employee job performance from a multisource perspective. It is also referred as a multisource assessment or a multi-rater feedback since it relies on information from various actors. Ideally a 360 degree feedback assessment is done by evaluating an employee job performance through a comprehensive investigation of their working relationship, from both an internal and external perspective. The idea is to generate an accurate assessment of an employee job skills, quality of work output and team work abilities that can be relied for employee assessment and job evaluation. The term “360 degree feedback” was introduced in the 1990-s as systematic collection of information on the results of an individual or a group obtained from the environment. It is intended to obtain an informative feedback from the manager, subordinates, peers and management. In some cases there may be used a Continue reading