Employee relations and management is an essential aspect of organisations. This cuts across organisations that prevailed in ancient days and the organisations in the modern days. Different models and perspectives have been adopted by various organisations to manage employees. The employee relations in organisations emerged amidst industrial relations which began in the 1920s in Europe. During this time, ‘industry’ was the term used to mean ‘the manufacturing firm’. However, in modern days, the meaning of the word has expanded to include the manufacturing firms and other sectors of the economy that do not deal with manufacturing. The definition of industrial and employee relations covers all forms and kinds of employment. Scholars in the field of industrial and work relations have come up with three management perspectives that differ significantly. These perspectives are different in their explanation, understanding and analysis of relations at places of work. These theories include the unitarist Continue reading
Human Resource Concepts
Causes of Low Levels of Workplace Productivity
Organizations which have goals to achieve require happy and satisfied staff. Organizational climate serves as a measure of individual feelings and perceptions about an organization. Organizational climate includes leadership styles or management, participation in decision making, provision of challenging jobs to employees, personnel policies, reduction of boredom and frustration, provision of good working conditions, provision of benefits and creation of suitable career ladder for academics, In case there is some form of dissatisfaction. The organizational climate is viewed as characterized by the following factors: Unchallenging jobs, lack of recognition for work done well through merit or announcements in meetings, shortage of personnel where they are expected to perform responsibilities, which were supposed to be performed by other employees, lack of feedback about performance, poor communication where there is no two-way communication between subordinates and managers and lack of staff development activities which prevent personnel from being equipped with skill and Continue reading
Integrating Balanced Scorecard (BSC) With Compensation Strategies
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is a tool utilized in corporations for the purpose of compensating workers in a way that is beneficial for both the management and the workforce. The Balanced Scorecard technique aids assessment of corporation performance in terms of monetary and non-monetary aspects. Connecting compensation to the Balanced Scorecard is useful because it acts as an equitable way of evaluating performance of companies by utilizing similar standards. The connection between company profitability and the amount of reward motivates employees to improve their performance. Realization of company’s goals is possible with the implementation of Balanced Scorecard and compensation. Usually, achievement of the goals and objectives of the company depends on the productivity of workers. Utilization of the Balanced Scorecard motivates workers to improve their performance and in turn achieve rewards. The linkage between the Balanced Scorecard and compensation operates well within the organization which possesses established quality programs. Assimilation Continue reading
360 Degree Feedback – Meaning, Process, Pros and Cons
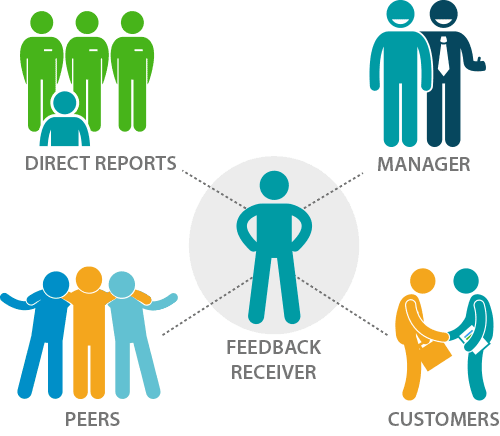
360 degree feedback is an assessment evaluation tool that is focused on employee job performance from a multisource perspective. It is also referred as a multisource assessment or a multi-rater feedback since it relies on information from various actors. Ideally a 360 degree feedback assessment is done by evaluating an employee job performance through a comprehensive investigation of their working relationship, from both an internal and external perspective. The idea is to generate an accurate assessment of an employee job skills, quality of work output and team work abilities that can be relied for employee assessment and job evaluation. The term “360 degree feedback” was introduced in the 1990-s as systematic collection of information on the results of an individual or a group obtained from the environment. It is intended to obtain an informative feedback from the manager, subordinates, peers and management. In some cases there may be used a Continue reading
360 Degree Performance Evaluation – Meaning, Process, Advantages and Disadvantages
Meaning and Process of 360 Degree Performance Evaluation Performance evaluations are an official interaction between managers and employees in which the manager assesses job performance and discusses in detail strengths, weaknesses and opportunities for development of the employee. Performance reviews serve as an important part of a human resource management systems. Measuring job performance, developing leadership skills, and designing a career path are the major uses of performance appraisal. Ideally, management conducts appraisals in an objective, consistent, and fair way. There are different forms of appraisals that organizations may choose to employ, including, 360 degree performance evaluation, management by objectives and a rating scale. A 360 degree performance evaluation (sometimes referred to as 360-degree feedback), utilizes input from oneself, colleagues, subordinates, and customers, as well as managerial feedback to complete the appraisal of job performance. The philosophy behind gaining feedback from a self-assessment and a variety of additional sources is Continue reading
Factors influencing wage and salary structure of an organization
The wage policies of different organization vary some what. Marginal units pay the minimum necessary to attract the required number of kind of labor. Often, these units pay minimum wage rates required by labor legislation, and recruit marginal labor. At the other extreme, some units pay well about going rates in the labor market. They do so to attract and retain the highest caliber of labor force. Some managers believe in the economy of higher wages. They feel that, by paying high wages, they would attract better workers who will produce more than average worker in the industry. This greater production per employee means greater output per man hour. Hence, labor costs may turn those existing in firms using marginal labor. Some units pay high wages because of a combination of a favorable product market demand, higher ability to pay and the bargaining power of trade union. But a large Continue reading