Performance management is assessing the process of achieving goals and objectives to unsure that it is successful through communication and taking the right action. There are functions for evaluating how equipments behave so that effective work is done through proper performing systems and altering the systems that do not perform well. In the organization, performance is looked at in terms of actual results for the improvement to be done if actual results are less than the desired results. Objectives should be set through proper planning and intervention of managers in giving feedback about the progress that has been made and ensure there is performance appraisal to individuals based on their overall contribution. Performance management is used by businesses to attain strategic goals through getting the necessary information for achieving the goals and have networking process that link objectives of individuals who make great contribution to the enterprise with the goals Continue reading
Human Resource Management Basics
Unitarist and Pluralist Perspectives in Human Resources Management
Employee relations and management is an essential aspect of organisations. This cuts across organisations that prevailed in ancient days and the organisations in the modern days. Different models and perspectives have been adopted by various organisations to manage employees. The employee relations in organisations emerged amidst industrial relations which began in the 1920s in Europe. During this time, ‘industry’ was the term used to mean ‘the manufacturing firm’. However, in modern days, the meaning of the word has expanded to include the manufacturing firms and other sectors of the economy that do not deal with manufacturing. The definition of industrial and employee relations covers all forms and kinds of employment. Scholars in the field of industrial and work relations have come up with three management perspectives that differ significantly. These perspectives are different in their explanation, understanding and analysis of relations at places of work. These theories include the unitarist Continue reading
Causes of Low Levels of Workplace Productivity
Organizations which have goals to achieve require happy and satisfied staff. Organizational climate serves as a measure of individual feelings and perceptions about an organization. Organizational climate includes leadership styles or management, participation in decision making, provision of challenging jobs to employees, personnel policies, reduction of boredom and frustration, provision of good working conditions, provision of benefits and creation of suitable career ladder for academics, In case there is some form of dissatisfaction. The organizational climate is viewed as characterized by the following factors: Unchallenging jobs, lack of recognition for work done well through merit or announcements in meetings, shortage of personnel where they are expected to perform responsibilities, which were supposed to be performed by other employees, lack of feedback about performance, poor communication where there is no two-way communication between subordinates and managers and lack of staff development activities which prevent personnel from being equipped with skill and Continue reading
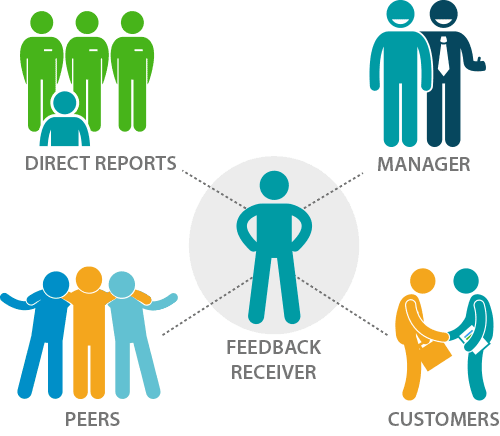
360 Degree Feedback – Meaning, Process, Pros and Cons
360 degree feedback is an assessment evaluation tool that is focused on employee job performance from a multisource perspective. It is also referred as a multisource assessment or a multi-rater feedback since it relies on information from various actors. Ideally a 360 degree feedback assessment is done by evaluating an employee job performance through a comprehensive investigation of their working relationship, from both an internal and external perspective. The idea is to generate an accurate assessment of an employee job skills, quality of work output and team work abilities that can be relied for employee assessment and job evaluation. The term “360 degree feedback” was introduced in the 1990-s as systematic collection of information on the results of an individual or a group obtained from the environment. It is intended to obtain an informative feedback from the manager, subordinates, peers and management. In some cases there may be used a Continue reading
Analytical Approaches to Cultural Factors
The reason cultural factors are a challenge to global marketers is that they are hidden from view. Because culture is learned behavior passed on from generation to generation, it is difficult for the inexperienced or untrained outsider to fathom. Becoming a global manager means learning how to let go of cultural assumptions. Failure to do so will hinder accurate understanding of the meaning and significance of the statements and behaviors of business associates from a different culture. For example, a person from a culture that encourages responsibility and initiative could experience misunderstandings with a client or boss from a culture that encourages bosses to remain in personal control of all activities. Such a boss would expect to be kept advised of a subordinate’s actions; the subordinate might be taking initiative on the mistaken assumption that the boss would appreciate a willingness to assume responsibility. 1. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs The Continue reading
Workforce Diversity Management in the Age of Globalization
Within each and every organization, the composition of workforce diversity is being integrated into its human resource management (HRM). In this new era, the world is increasingly globalizing and since the advent of information technology, the borders of the world are drawn so closely than ever before. Theories of diversity management have been developed by business professionals and scholars, citing that a heterogeneous organization could create better HRM practices to maximize the benefits from a diverse workforce as well as improving their competitive advantages. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs will help to understand how employees’ basic need affects the HRM; and how workforce diversity could contribute to achieving HRM’s strategic objectives. Diversity awareness allows for a better understanding of inclusive consumers’ needs, and provides access to better labor pools. Hence, an organization must be able to utilize the available skills from the workforce if it is to maintain competitive advantage and Continue reading