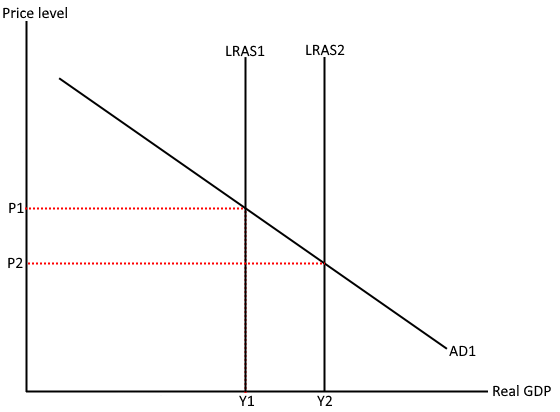
The supply side policies entail the attempts undertaken by governments in an effort to stimulate productivity and ensure that the long-term aggregate supply [LRAS] curve shifts to the right as illustrated in graph 1 below. The outward shift of the LRAS curve leads to an increase in the potential output. From the graph, the shift in the LRAS to LRAS2 leads to an increase in the size of the output from Y1 to Y2. The supply side policies are focused on stimulating a country’s productive capacity. Labor productivity is one of the most important elements in the supply side policies. The policies underscore the importance of establishing flexible labor markets. Despite the flexibility aspect, the role of the government in the implementation of the supply side policies cannot be ruled out. In some instances, government intervention is necessary in order to overcome market failure. The objective of the supply side Continue reading
International Economics
Different Approaches to Profit in Managerial Economics
Profit is the reward which goes to organization as a factor of production for its participation in the process of production. Profits differ from other factor rewards in the following ways: Profit is a residual income left after the payment of contractual rewards to other factors of production. The entrepreneur while hiring other factors of production enters into contract with them. He pays wages to workers, rent for land and interest for borrowed capital and the residue or whatever is left is his profit. Thus profits become non-contractual in character. The various factors of production are rewarded even before the sale of the product and irrespective of its sales whereas profits accrue only after the product is sold. The rewards of other factors have been fixed. They do not fluctuate whereas profits go on fluctuating so much so that the entrepreneur bears the risk of even incurring losses which we Continue reading
Relevance of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) for Businesses and Organizations
The organizations have been focused towards adopting key business approaches and practices that would contribute towards their improved revenue as well as profitability in the marketplace. In order to achieve such strategic goals to revenue and operational growth, it is required by the management to identify and understand the changing market needs, as well as the stakeholder preferences and accordingly the internal business or operational strategies, are to be defined. Considering such need, it can be reflected that in the present marketplace there is a need for the business organization to focus towards the increased social preferences and need towards sustainability and societal development along with that of the business growth. The approach to sustainability ensures that the business organization have a balanced approach towards society, business as well as the environment. Further to strengthen the approach to sustainability international organizations including United Nations (UN) has defined several key sustainable Continue reading
Transformation of The European Union From a Political and Economic Union to a Monetary Union
The basis of the European Monetary Union was to build a united Europe after the World War II. This was initiated by when the European nations created the European Coal and Steel community, with a view to freeing trade in these two sectors. The pricing policies and commercial practices of the member nations of this community were regulated by a supranational agency. In 1957, the Treaty of Rome was signed by Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, Luxemburg and the Netherlands to form the European Economic Community (EEC), whereby they agreed to make Europe a common market. While they agreed to lift restrictions on movements of all factors of production and to harmonize domestic policies, the ultimate aim was economic integration. The EEC achieved the status of a customs union by 1968. In the same year, it adopted a Common Agricultural Policy (CAP), under which uniform prices were set for farm products Continue reading
National Income Statistics: Meaning and Uses
What is National Income Statistics? According to most dictionaries, national income is literally the total amount of money earned by a certain country. But in order to calculate the total funds and asset of the country, National Income Statistics are used, which are basically a set of rules, techniques and calculation to measure the total value of final goods and services produced. However, The National Income Statistics are only valid to calculate the national income of a country in a year. The Uses of National Income Statistics Like every other calculations, The National Income Statistics also have their own uses. The National Income Statistics are very important to the development of a certain country as it is the result of hard works done in a year to contribute in the enhancement of a certain country. Firstly, as we all know money and riches usually determines the standard of living of Continue reading
Trade Theory of Independence, Interdependence and Dependence
Independence — Interdependence — Dependence Theory of International Trade tries to read trade patterns and policies of countries based on their degree of independence or dependence or interdependence on rest of the world. See this is a continuum: Independence — Interdependence — Dependence. The polar extremes are Independence at one pole and Dependence at the other. Independence stops trade, while dependence boosts trade. Independence: Independence is being self-reliant. Well one cannot be self-reliant. Yet one country may choose to be independent and the cost of such obstinacy is self-denial of life’s luxuries, comforts and necessities that can be afforded without difficulty. It may be a government policy to remain independent. This austerity could cost the country heavily. Hence governments plan independence sans difficulty for citizens. Few countries in the world maintain a vast reserve of essential minerals and even don’t touch own oil fields, so that in future if foreign Continue reading