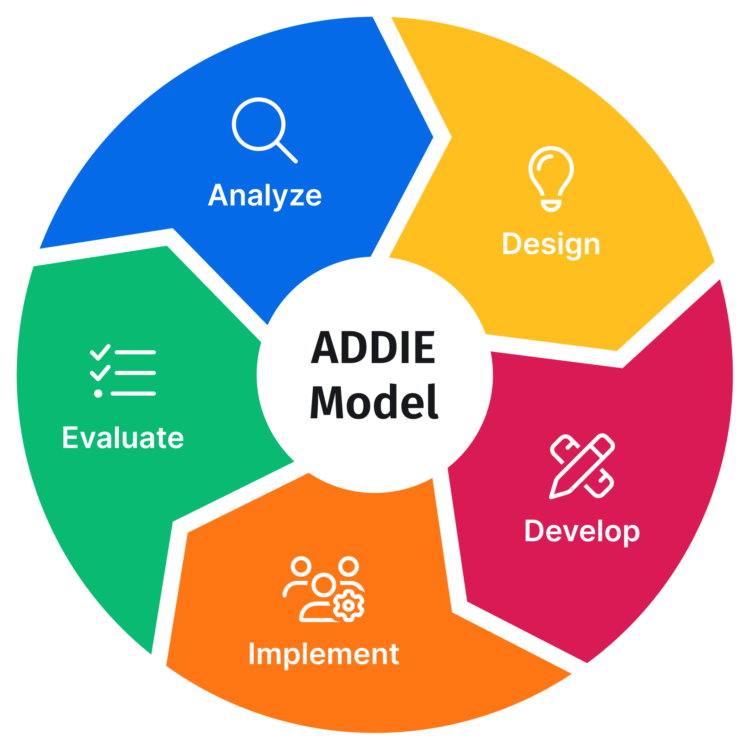
Instructional design denotes the process through which tutors or other relevant education stakeholders improve instruction through the systematic development of teaching materials to respond to the identified learning requirements. It is also referred to as instructional systems design. To guide the process of instructional design, many approaches have been suggested and their effectiveness supported and criticized in equal measure. One of the most popular instructional system design models is the ADDIE model, which represents five phases of the instructional design process. The phases comprise the Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation stages It is important to know and understand the ADDIE model if a training development program is to be successful. ADDIE model is an extremely effective tool in training development that addresses instruction. Most employees have a significant amount of information to learn in order to become more proficient at their jobs. Therefore, the ADDIE model could be quite Continue reading
Modern HRM
Employee Reward Management – Meaning, Components, Process, and Issues
Reward management entails the formulation, maintenance, communication and evaluation of reward processes that assist an organization in enhancing its performance as well as achieve its objectives. Successful organizations manage their reward practices in such a way that enables them to come up with accurate predictions with regards to what innovations are best suited for the organization as well as ensuring that whatever activities that they engaged in currently will assist them in delivering the expected results. Such organizations strive to avoid ‘folly of rewarding A while hoping for B’. These organizations opt for the evidence based management approach. Evidence-based reward management refers to the kind of management approach that is justified by improvement in the organization’s performance. In other words, it implies that the effectiveness of the reward management approach can be measured against a certain set of indicators to ascertain whether they have impacted the performance of the organization in Continue reading
Achieving Sustained Competitive Advantage Through Strategic HR Management
Human resource management (HRM) is the art of managing employees in an organization. It involves the use of people to achieve organizational objectives in a productive manner and still satisfy the needs of individual employees. This is the traditional approach to human resource management. Human resource management has always been viewed as a department set apart from the rest of the organization. Lately however, the human resource department has had to justify its existence within an organization due to the increase in use of technology in place of human resources. The move is an attempt by the HR department to remain relevant to an organization in the face of the current technological changes. This has led to the emergence of Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM). SHRM is a form of management that links HRM with organizational goals and objectives to improve performance and to strengthen organizational culture. SHRM focuses on organizational Continue reading
Trompenaar’s Four Types of Corporate Management Culture
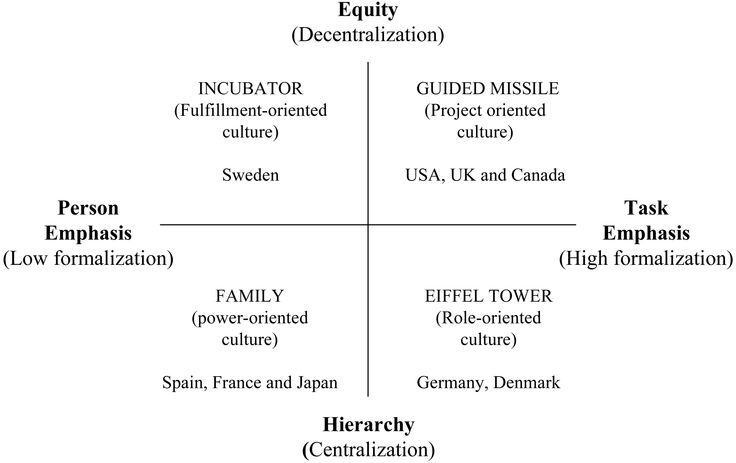
Nowadays, the effectiveness and growth prospects of international companies directly depend on the development of internal corporate culture. After studying such aspects of the work of large organizations as the relationship between employees, the subordination system in the company, and employees’ attitudes and views on the development of the MNCs, Alfonsus (Fons) Trompenaars (Dutch organizational theorist, management consultant, and author in the field of ethics) states that the fundamental orientation should be on the personality and objectives of the company. Thereby, the scientist identified four types of corporate management culture, which received symbolic names: family, guided missile, incubator, and Eiffel Tower. 1. Family Culture The family type of culture is strictly hierarchical and focuses on the execution of instructions from leaders. The system as a whole is based on a paternalistic attitude: the initiative and efforts of subordinates should correspond to the leadership’s goals, but people do not call the functions Continue reading
Donald Super’s Career Development Theory
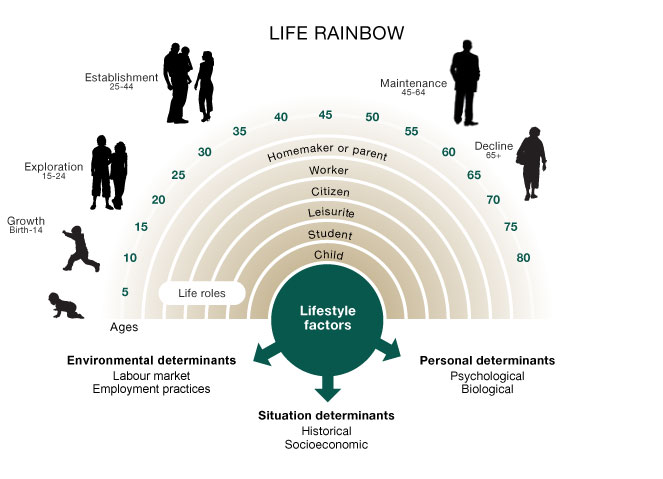
Career theories are usually based on circumstances such as social, economical and environmental. The modern concept of career is a product of the industrial age. Traditionally, organizations would structure people’s career paths and lives. During these times, work was concentrated in employment, learning was concentrated in education and education gave way to employment. Career counseling was a concept introduced to the education systems to help individuals transit from one sector (education) to another. Continuous improvement in career was viewed as a lifelong process. Donald Super in 1953 shed light on this idea and proposed a theory. Holland in 1956 expanded on the psychology of personality in relation to career development and career choice. These two theories in particular and multiple others have included psychological and social aspects to the understanding of the career choices that people make. Career theories look at the complexity of career choice, adjustment and development. Donald Super’s Continue reading
Case Study of Disneyland: An Intermediary Between Diverse Cultures
Since the first of the Disney parks was founded in 1955 in Anaheim, California, Disneyland theme parks have often been referred to as the “happiest places on earth.” Disneyland’s are recognized worldwide for their joy-filled rides, playful atmosphere, and other amusement features. Various studies have shown that Disneyland has created multicultural amusement zones where people from diverse geographic and cultural backgrounds enjoy escapism and fairy-tale life. This description makes Disneyland an intermediary between cultures. Culture can be seen as shared beliefs, customs, values, behavioral patterns, and cognitive constructs among people belonging to a particular group. It defines the characteristics and knowledge of unique groups of people in aspects such as language, socialism, religion, cuisine, art, and more. While culture presents diverse characteristics among people of different origins, conscience plays a significant role in binding them within a larger society, allowing them to share unique experiences, beliefs, attitudes, values, spatial relations, Continue reading