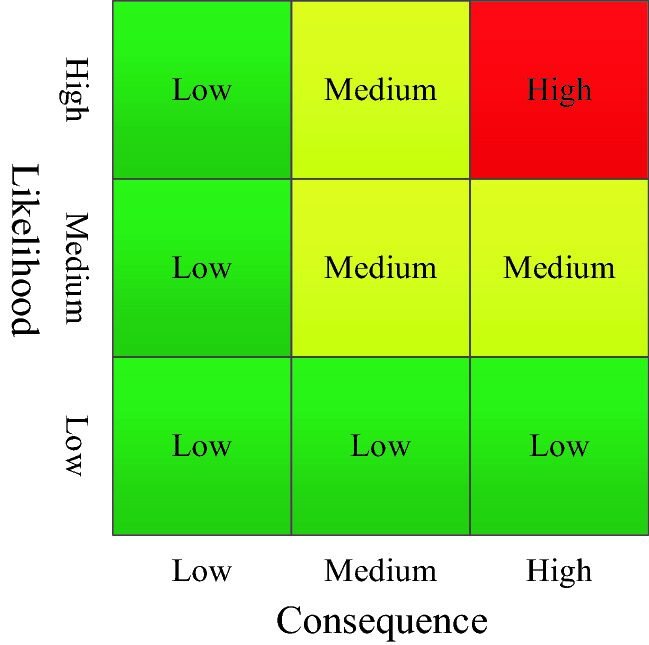
A risk matrix is defined as a table that is divided into several categories of probability, likelihood, or frequency for its rows, and multiple categories of severity, impact, or consequences for its columns. The constituents of risk ordinarily attest themselves as a hazard; which refers to the likely origin of a harmful outcome and harms; which are the ensuing damages to the environment. It incorporates generally accepted ratings of risk, urgency and priority, with every row-column pair. This is represented by distinct cells which are separately colored, using red, green and yellow colors. Each distinct cell has a different risk rating, for instance, cells colored in red will indicate risks that require an urgent attention, whereas those that are colored in green will indicate those risks that do not require to be dealt with urgently. The yellow colored cells indicate those risks that fall in between the ratings of very urgent and Continue reading
Modern Management Approaches
Sharing Economy Concept – Meaning, Drivers, Principles, and Forms
“Sharing economy” is the term that entered scientific literature not so long ago that is why it is still rarely used. Being also known as ‘collaborative economy’, this term is used to describe a type of business model that builds on the sharing of resources between individuals through peer-2-peer services – allowing customers to access goods and services when needed. The transaction between individuals takes place through sharing economy firms, which are called intermediaries. The intermediaries provide the platform, such as a website or a smartphone app, rather than providing the service directly. Sharing economy firms started to appear in 2008 and 2010, in the aftermath of the global financial crisis, which prompted people to look for new business opportunities. As a business model, the sharing economy takes different forms and is characterized by unique features. More and more people and organizations become involved in the sharing processes currently. The Continue reading
The Role of Emotional Intelligence in the Hiring Process
There are several types of jobs where emotional intelligence (EI) assessment could be effective in personnel selection. Moreover, high EI is necessary for highly demanding jobs. For instance, lawyers and file clerk, who face a lot of emotional labor during their day-to-day work, may fake their chances of securing a job position or use interpersonal interactions. However, such jobs as accountants and welders, which have little to no emotional labor, do not depend on emotional skills. HR professionals may not effectively measure or predict EI via testing methods. For instance, on the psychometric test for EI, it is impossible to predict EI as it is a measure of cognitive intelligence rather than EI. The use of practice employment tests is significant in improving recruitment and personnel selection outcomes for highly demanding job positions. Therefore, HR professionals who are ardent about using psychometric tests for EI may discover that they are Continue reading
The Importance of Emotional Intelligence
The concept of emotional intelligence (EI) is an integral part of all areas of human development. However, as with many other scientific ideas, scientists still cannot agree on what emotional intelligence is. There are many definitions of emotional intelligence. Some define emotional intelligence as a set of non-cognitive abilities, competencies, and skills that affect a person’s ability to cope with challenges and environmental pressure. Others see this as the ability to be aware of their emotions and the emotions of others in order to motivate themselves and others and to manage emotions well in private with themselves and when interacting with others. Since the trainer is more a practitioner than a scientist, a shorter definition is preferred, which is easier to work with during the training and which conveys the essence of this scientific concept. Emotional intelligence is the ability to be aware of one’s emotions and the feelings of Continue reading
The Importance of Emotional Intelligence for Leaders
Leaders need to have traits that are visionary and should be competent enough to attain the intended goals of the organization; meaning that the future of the organization lies squarely on the ideas generated by them. Such people should be inspired and possess the capability to explain it to the rest of the leaders or work mates. For a leader to induce change in an organization, there are issues that he or she needs to be well versed in. While taking care of issues that arise from the management, some challenges are evident especially those that touch on the management criteria of the organization. Leaders should know that it is important to understand the success they achieve in an organization results from teamwork and should not be credited to specific individuals. In addition, managers should be prepared to let go of outdated cultures or practices in the company; this means Continue reading
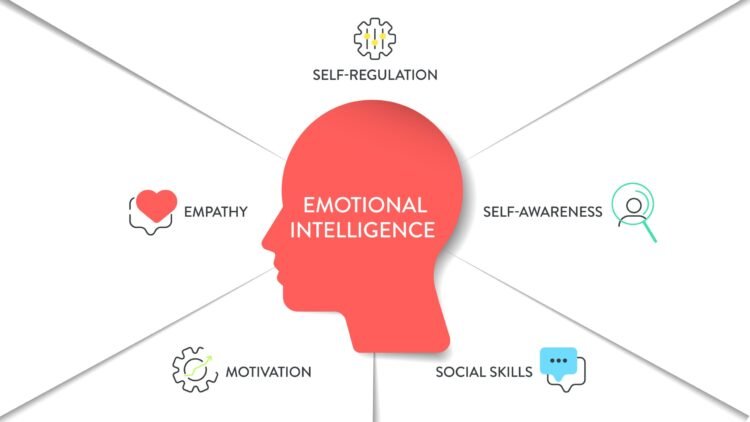
The Five Components or Competences of Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence is the ability of an individual to recognize their own feelings, those of other people, in order to motivate one self and as well be able to manage our emotions, in our own self and in the relationships that we are having with other people. Times back, emotional intelligence was never recognised but as times goes it has been realised that emotional intelligence is a very important thing in the workplace today. It has been realised also that the IQ that an individual has, or having a high IQ does not matter and it does not guarantee a successful business. From Daniel Goleman’s book on working with emotional intelligence, we are able to see that most of the outstanding performers in the areas of business and great business leaders are mainly defined in the areas of their jobs by their “emotional intelligence” and not exactly by their job Continue reading