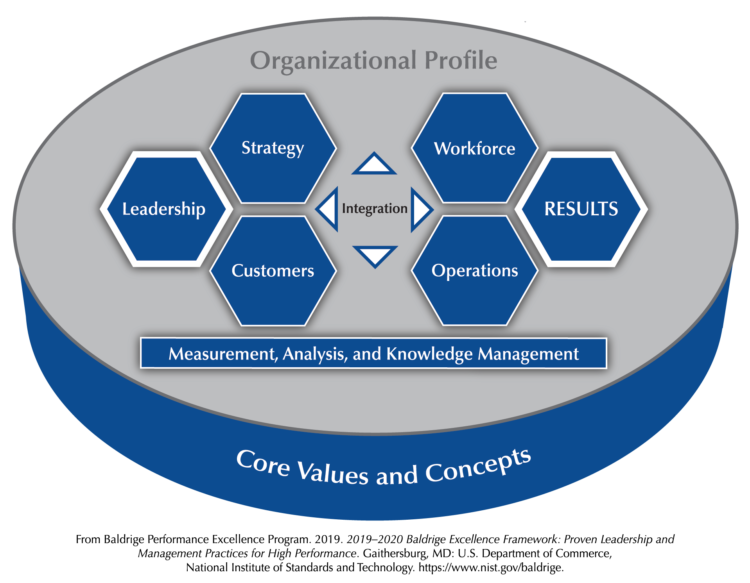
In the business world, the realization of business excellence is pivotal towards fostering the success of an enterprise. In this respect, business organizations need to engage in actions that facilitate performance excellence. The areas of business operations that need a considerable extent of excellence include customer satisfaction, workforce fulfillment, operations efficiency, and business growth. The need for continuous improvement influences business managers to adopt the suitable performance excellence models. The Baldrige Excellence Framework is one of the most sought-after performance excellence models that drive the success of businesses in different sectors. The model mainly focuses on bolstering performance excellence by improving the business aspects of leadership, strategic planning, customer supervision, workforce administration, knowledge management, and operations focus. Business organizations need to focus on improving the performance of the mentioned aspects to realize significant excellence in their respective industries. Background In the mid-1980s, leaders in the United States saw the need Continue reading
Production Management Concepts
Fordism – Meaning, Concept, Contributions, and Critiques
Economists and philosophers have developed many theories that explain how organizations are managed and how they function. Managers look upon these theories when they are managing the organization. The theories have impacts on the organization in which they are applied. The impacts could either be positive or negative depending on how it is applied and the form and nature of organization in which it is applied. In fact, each theory has its strengths as well as shortcomings. It is, therefore, the duty of the managers to choose the theory that best fits their organization and that which contributes to organizational success. Among the theorists who have contributed to the theories that have had significant impacts on organizations is Henry Ford. Henry Ford is one of the most celebrated industrialists of all times. He is the one who founded the famous motor company known as Ford Motor Company, named after him. Continue reading
Post-Fordism – A Critical Evaluation
It is widely argued that the era of Fordism began with the development of the model T motor car, the world’s first successfully mass-produced car, at Henry Ford’s Piquette Avenue manufacturing plant in Detroit, Michigan. From this, a new age of production developed, changing both the economic and the political landscape of manufacturing globally, and establishing the progression to a new form of capitalism. The key characteristics of Fordism center around the major industrial paradigm of mass production that involves production of standardized goods by unskilled labor through the use of assembly-line techniques. This principle of ‘continuous-flow production’ as a new regime of accumulation inherently involved a rise in mass consumerism, that was encouraged by the supply of relatively cheap products, intelligent advertising and, arguably most importantly, through changes to social conditions of low-skilled employees. This originated from Henry Ford himself, who notoriously raised minimum pay to $5 a day Continue reading
Concurrent Engineering Vs Traditional (Sequential) Engineering Methods
Traditionally, products were designed and manufactured following the sequential engineering methods, where people from different departments work one after the other on successive phases of development. This method of production is in a linear format. The different steps are done one after another, with all attention and resources focused on that one task. After it is completed it is left alone and everything is concentrated on the next task. The product is first completely defined by the engineering design department, and then the manufacturing department take over and define the manufacturing process, etc. This was a lengthy process, and often led to a lot of design changes as the prototype testing began, due to production problems, delays or design flaws. This is therefore a slow and costly approach, often leading to a low-quality and less competitive product. Concurrent Engineering, sometimes called Simultaneous Engineering or Integrated Product Development (IPD), can be Continue reading
Deming’s System of Profound Knowledge – 14 Principles
William Edwards Deming (1900-1993) was a renowned American quality management consultant, professor, and statistician, and wrote several books on product quality and management and gave lectures on the same. He is attributed for helping to advancement in production in corporate America but his greatest achievements were in Japan. He made a major contribution to Japan’s a trade and industry development, and also the advancement of their high-quality products. Deming (1990) noted that “by adopting appropriate principles of management, organizations could increase quality and simultaneously reduce costs (by reducing waste, rework, staff attrition and litigation while increasing customer loyalty).” Deming recommended that organizations should focus on quality which leads to reduction of costs, instead of concentrating on costs that decrease the quality gradually. He mostly advocated for proper management as he argued that it was responsible for 85% of the problems that companies face. He argued that good management of an Continue reading
Plant Layout Crtierias and Basic Designs
The layout of a plant or facility is concerned with the physical placement of resources such as equipment and storage facilities, which should be designed to facilitate the efficient flow of customers or materials through the manufacturing or service system. The layout design is very important and should be taken very seriously as it can have a significant impact on the cost and efficiency of an operation and can involve substantial investment in time and money. The decisions taken with regards to the facility layout will have a direct influence on how efficiently workers will be able to carry out their jobs, how much and how fast goods can be produced, how difficult it is to automate a system, and how the system in place would be able to respond to any changes with regards to product or service design, product mix, or demand volume. In many operations the installation Continue reading