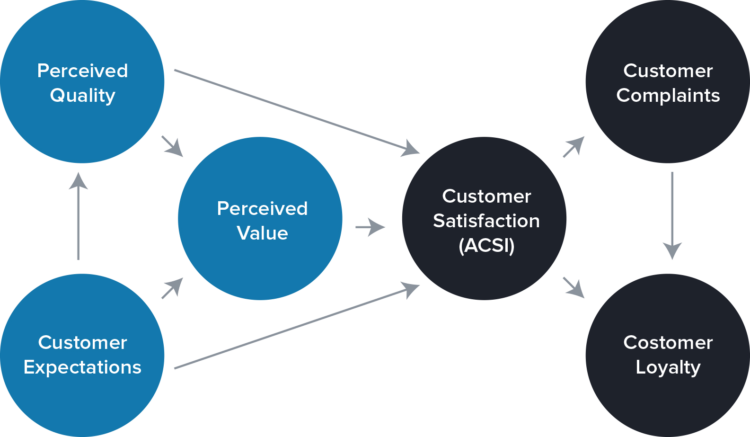
The Customer Satisfaction Model is a set of causal equations that link perceived quality, perceived value and customer expectations to customer satisfaction. The customer satisfaction model is linked, in turn, to its consequences in terms of customer complaints and customer loyalty. This model is based on the American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI), which is one of the best-in-breed solutions for customer satisfaction measurement that is tied directly to financial performance. The American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI) is the leading national indicator of customer satisfaction with goods and services in the U.S. economy. The ACSI was developed by the University of Michigan’s Stephen M. Ross School of Business. The dependent variable in this conceptual model is customer satisfaction, while the independent variables are perceived quality, perceived value and customer expectations. Customer complaints and customer loyalty are the results (consequences) of this conceptual framework. Perceived quality is the first determinant of customer satisfaction, Continue reading
Services Marketing Concepts
The SERVQUAL Model – Definition, Dimensions, Gaps, Advantages and Disadvantages
Knowing the customer(s) is the key to a successful customer service as the idea is to create, deliver and communicate superior value. The service and/or products offer should answer to the needs and demands. Customers are the most important people for any organization. They are the resources upon which the success of the business depends. Understanding customers are necessary not only because of their effect on marketing decisions but because customers’ activities influence the entire organization. When thinking about the importance of customers it’s useful to remember the following points: Repeat business is the backbone of selling. It helps to provide revenue and certainty for the business; Organizations are dependent upon their customers. If they do not develop customer loyalty and satisfaction, they could lose their customers; Without customers the organization would not exist; The purpose of the organization is to fulfill the needs of the customers; The customer makes Continue reading
Services Marketing Mix – The 7 P’s of Services Marketing
Marketing mix is the key concept in the marketing task. It is the strategy used to perform marketing functions. Marketing mix is the planned package of elements which will support the organization in reaching its target markets and specific objectives. The common factor behind all the elements of marketing mix is that they are specific parameters which the marketing manager can exercise some control over, within the constraints of their firm’s resources. For example, the marketing manager can control the type of product to be developed, subject to the firm’s technology, as well as the places it is sold, subject to the firm’s distribution network. Ultimately, the aim of the marketing mix is to ensure that all P’s are focused on the target customers, serving their needs and creating value for them Elements of Services Marketing Mix The services marketing mix is also known as an extended marketing mix and Continue reading
Services Marketing Triangle
A service is any act or performance that one party can offer to another that is essentially intangible and does not result in the ownership of anything. Its production may or may not be tied to a physical product. Furthermore, service marketing can be defined as the marketing of activities and processes rather than objects. As services are mainly intangible products, they face a host of services marketing problems that are not always adequately solved by traditional goods-related marketing solutions. Services Marketing Triangle The services marketing triangle was created to handle the complexity that service marketers face when dealing with intangible products. The service marketing triangle highlights three key players, these are; Company: The management of a company, including full-time marketers and sales personnel. This is enabled through continuous development and internal marketing with their employees. Employees: This includes anyone that is working within close contact of the consumer. They Continue reading
The Service Recovery Paradox
The present key business strategy eyes on keeping the current customers and developing relationships with the new ones. Providing services to the customers or the consumers is very difficult. Unfortunately the services provided to the customers can never be perfect, the failure can be due to unprompted employee actions, failure to respond to specific customer needs or also due to core service facilities. Hence the companies try their best to reduce the mistakes from repeating again and in satisfying the customers needs. This article discusses about the “service recovery paradox” steps that is being followed by the organizations to recover from their service failures. According to McCollough and Bharadwaj 2002, service recovery paradox can be said as the situation at which the customers post failure expectations exceed pre failure expectations. This is like the organization taking preventive steps to satisfy their customers by reducing their failures and also in not Continue reading
Impact of Service-Dominant Logic on Strategic Marketing and Relationship Marketing
The Stephen Vargo and Robert Lusch paper “Evolving to a New Dominant Logic for Marketing” (2004, Journal of Marketing) redefines and redirects the age-old economic view of goods and services. Their paper states, “Over the past several decades, marketing has been evolving toward a new dominant logic… The evolving logic represents a shift away from the exchange of tangible output (goods) toward the exchange of services, which are defined as the application of specialized competences (knowledge and skills), through deeds, processes, and performances for the benefit of another entity or the entity itself.” This philosophy of marketing argues that firms are not really providing goods, but are actually rendering a service to consumers through their goods. This new service-dominant logic view of marketing has already made a huge impact on both the strategic marketing and relationship marketing of firms and will continue to further impact future marketing strategy. For nearly Continue reading