Development and expansion organizations’ core competency is one of the main success factors of many organizations. However, if organizations do not apply correct measures when transferring core competencies for one business to another, the likelihood of failure is high. Transfer of core competencies is one of the most important business diversification strategies of ensuring organizations reduce costs of starting over again in new business ventures. Transferring core competencies and resource strengths from one country market to another is a good way for companies to develop broader or deeper competencies and competitive capabilities that can become a strong basis for sustainable competitive advantage. It mostly works via capitalizing on operational relatedness, primarily applying the constrained multi-product strategy. This strategy offers organizations a chance of realizing and exploiting economies of scope, a crucial pathway for gaining a competitive advantage over other businesses. In addition, it guarantees organizations opportunities for utilizing existing expertise Continue reading
Strategic Management Basics
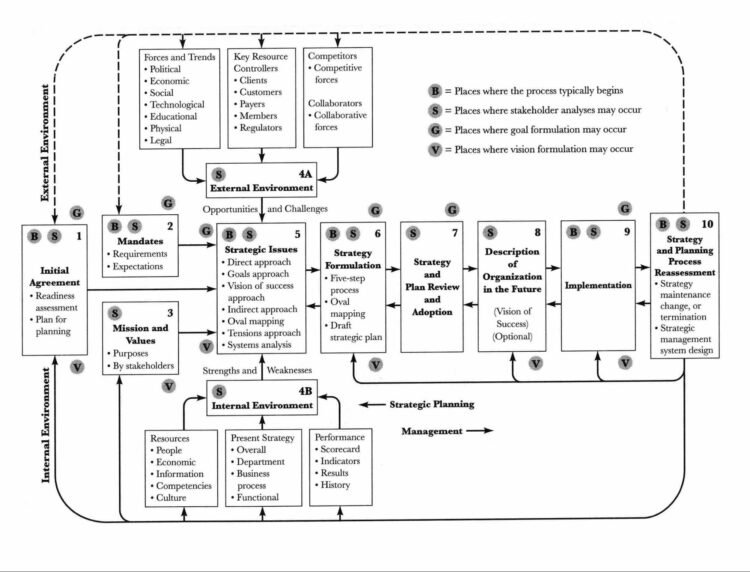
Strategic Management Model: Bryson’s Strategy Change Cycle for Strategic Planning
In ensuring effective strategic change in an organization, strategic planning is inevitable for organizations to develop and implement strategies through the strategy change cycle. A strategic change cycle is a systematic procedure that is indispensable in determining whether an organization will be successful. The strategy change cycle is among the primary processes of strategic management that links the processes of planning and implementation and ensures that the process is carried out consistently and in alignment with specific organizational goals. The following section discusses ten vertical steps in the change cycle by keenly describing why they are essential for organizations in planning and implementing their strategies. Its purpose is to develop a consistent commitment to the mission and vision of an organization, both internally and externally, at the same time with maintaining a clear focus on the organizational agenda with the help of relevant activities and decision-making processes. Strategy Change Cycle Continue reading
Business Strategy Implementation
The business strategy will be implemented through the concerted actions of all staff working within a partnership framework. The Board will set objectives and parameters, for the business strategy implementation, and will review progress in achieving objectives. Management will take ownership, give leadership and agree with staff clearly defined roles and responsibilities in achieving targets and milestones. It is also recognized that resources issues may affect the full implementation of the strategy. To assist management in carrying out its role in delivering the strategy and whatever may evolve in the future, an integrated management development programme, with a particular focus on business planning and performance management, will a particular focus on business planning and performance management, will be provided. It is anticipated that other issues will emerge as the process evolves. The project groups will comprise of management and staff, at all levels, who have expressed an interest, and who Continue reading
Business Level Strategy vs Corporate Level Strategy
Business level strategy is defined as an organizational strategy that seeks to determine how an organization should compete in each of its businesses. In contrast, corporate level strategy is an organizational strategy that seeks to determine what business a company should be or wants to be. At the heart of business level strategy is the role of competitive advantage. This is what sets a company apart from its competitors and gives it a distinct edge. Sustaining competitive advantage will be based on the interplay of the five forces in an industry. According to Porter (1990), these five forces are the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitutes, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers and rivalry among firms. By performing an industrial and internal analysis, a firm can then identify its competitive advantages so that it can pursue the right strategy. There are a few major Continue reading
Role of Employee Involvement in Organizational Change
Employee involvement is known as the direct involvement of the organizational staffs in the growth, development and benefits of the company. This involvement can be with voice, participation, engagement and in democracy. These factors help the organization to improve its decision-making, improve the attitude of the employees towards work, increase the job satisfaction, and empower their employees with facilities for better health and life. To engage the employee in the organization, they should be given with the authority to become effective to take participate in substantive decisions, providing the training for appropriate decision-making skills and provide them rewards or incentives with successful participation. On the other hand, the organizational change is a process that refers to the modification or transformation of the organizations structure, work culture and goods. It has impact on the working of the employees and can also affect the work culture, infrastructure or to the process of Continue reading
Relationship Between Firm Performance and Competitive Advantage
The firm performance is a complex term which may include different shadows of meaning as long as it relates to organizational performance, functioning of the firm and outcomes of its operations. Normally, the firm performance implies the organizational performance, including manufacturing of products and services, functioning of different units of the firm, performance of its employees and outcomes of their work in total. At the same time, the firm performance can be viewed in a broader context as a part of the business development of the firm. What is meant here is the fact that the business development mirrors the firm’s performance and allows to assess the extent to which the organizational performance is effective. At this point, it is important to place emphasis on the fact that the firm’s performance is basically measured in terms of efficiency of the firm’s operations. In fact, the more effective the firm’s operations Continue reading