In recent years, the conditions of competition in the global environment have changed for the companies. The market is dominated by constant change, complex tasks and environmental turbulence. As knowledge, innovation and flexibility become an important resource for sustained competitive advantage and ‘Entrepreneurship’ is the crucial factor for success or survival. While small firms take the advantage of these conditions and become very successful due to their flexible structure and entrepreneurial spirit, large firms suffer more due to their mechanistic, bureaucratic and rigid structures. One of the solutions for companies to deal with the rigid bureaucratic structures is to induce Corporate Entrepreneurship in their structure. While CEOs are concerned about profitable organic growth, they find corporate entrepreneurship or creating a new business as one of the solution. As corporate entrepreneurship is becoming popular, it can be seen as a school within entrepreneurship theory. Since there is no generally accepted definition Continue reading
Strategic Management Concepts
Competitive Advantage of First Mover and Late Mover Strategies
Nowadays due to technology advancement, the way of how businesses were conducted has evolved to be more globally attributed and dependable to technological innovation aids. Furthermore, technology could help a firm to be sustained by having competitive advantage, and this especially true in the situation of where firm had the strong dependency towards technology innovation. Technology had becomes more important to specific firm or business when it has the ability to significantly affect their competitive advantage or industry structure. Thus, it is important for firms to choose and execute their strategy systematically to stay competitive and sustainable in the market. There are 3 ways of how first-mover could achieve their advantages. The first sources of how first-mover competitive advantage could be triggered are (i) technological leadership, (ii) preemption of assets, and (iii) buyer switching cost. Technological leadership will benefit first-mover in term of leadership in innovation, which ensure the sustainability Continue reading
Business Failure – Concepts and Prevention Methods
Most of the times, businesses fail to achieve the set objectives. Such a scenario comes about perhaps because the business does not implement the right strategies or offers customers a product that is not in demand. In addition, a business may fail because it is not located in a suitable environment. However, no matter what the causes of business failure are, many people tend to embrace different ideas on how failure is good for a business. This has been adopted by many people such that even organizations are adopting strategies that advocate for failure in business with the belief that failure is a step to the achievement of any set goals and objectives. The assertion that failure and fast failure is a good thing has received different opinions. Several people argue that failure in a business is a good thing while others are for the belief that failure is bad Continue reading
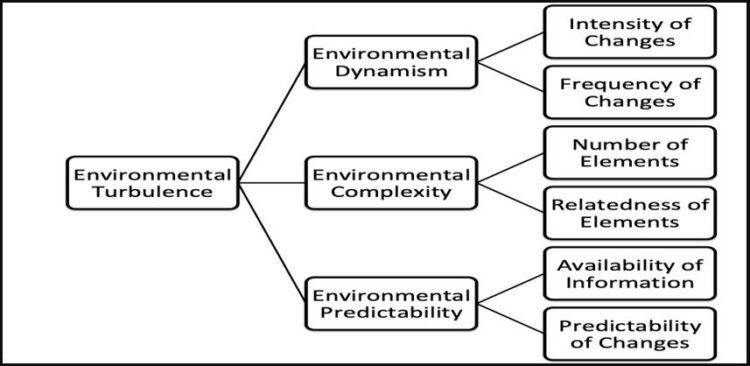
Environmental Turbulence Concept in Strategic Management
Business environments are described or analysed in various ways based on disparate important dimensions. However, the concept of turbulence is ambiguous. This confusion touches on the varying orientations in studying organisational environments and the diverse methods that are used to measure it. Environmental turbulence underscores the extent of change and degree of complexity in a business environment. Changes in technology, statutory regulations, or environmental factors are some of the examples that constitute environmental turbulence. Therefore, a turbulent environment is dynamic, expanding, unpredictable, and fluctuating. In addition, such an environment displays high levels of interconnectedness with the business. Turbulence is a complex interaction of several dimensions that are related to change where some elements dominate others or overlap each other at times. The figure below shows the configuration of the main dimensions of environmental turbulence. 1. Dynamism If the components of the tasks of the environment are highly variable, the business needs Continue reading
Internal and External Influences on Business Environment
In today’s dynamic business environment, organisations are subject to a myriad of influences that shape their operations, strategies, and overall performance. These influences can be broadly categorised into internal and external factors, each playing a crucial role in determining a company’s success or failure. By understanding these influences, businesses can develop robust strategies to navigate challenges and capitalise on opportunities in an ever-changing marketplace. Internal Influences on Business Environment 1. Organisational Structure and Culture One of the most significant internal influences on a business is its organisational structure and culture. The way a company is structured can greatly impact its efficiency, decision-making processes, and overall performance. Organisational structure defines how tasks are formally divided, grouped, and coordinated within a company. A well-designed structure can facilitate communication, enhance productivity, and foster innovation. Conversely, a poorly designed structure may lead to inefficiencies, conflicts, and reduced performance. Organisational culture, on the other hand, refers Continue reading
The Relationship between Sustainability and Innovation
Advancement in technology and the changing lifestyles of people requires flexibility and adaptation for business to survive. Technology has affected the way business is conducted around the globe. Opportunities present are friendly to innovative people who are able to come up with different strategies to solve problems that face human beings. Innovation and sustainability have become pertinent in business’ success. Concept of Sustainability Sustainability is a term used in reference to the need to conserve natural environments. It therefore implies that all things that are important to people’s lives depend on the environment. People thrive and survive because of their environment, which allows them to gain access to water and other important resources that are pertinent to their general life ad health. Therefore, ensuring that these environments are conserved should be their obligation. Businesses and individuals need to take the initiative of ensuring that the surrounding environment is protected from bad Continue reading