There exists several factors which contribute to the growth and success of an enterprise and among the leading factors is the age of the firm. To explain why smaller and younger firms are likely to grow faster than old and large enterprises is explained in economics by the use of the concavity of the production function. Where at the start, the small capital invested has the capability of multiplying exponentially but as time moves on and new investments are injected in to the investment, the marginal rate of productivity of the invested capital declines and that explains the reason why young firms grow faster than old and already established enterprises. Although many experts indicate that as the firm ages the likelihood of it learning form its mistakes and thus succeeding are high, the multiplier effect of large business is low and this is a major contributor to the success of an Continue reading
Strategic Management Concepts
Major Theories of Mergers and Acquisitions
Nowadays, the business world is looking for continuous expansion to generate higher revenues and enhancing the quality of the production processes. Additionally, mergers and acquisitions contribute to the strengthening of the competences and stimulation of the core competitive advantage while facing the increasing and intense competition in the world. Nonetheless, the significant differences between mergers and acquisitions tend to exist due to the different nature of the phenomenon. The takeover and acquisition imply having control of the acquired firm’s equity by 50 %. In turn, the merger implies the creation of the new business unit. Despite having slightly dissimilar nature, the intentions remain the same, as they remain an essential instrument to stay competitive on the market. In turn, the concept of the synergy enhancement also has to be taking into account while improving the quality of acquisitions and justifying their importance. It is commonly known that one of the Continue reading
Person-Environment Fit – A Theoretical Perspective
Organisational theory is essential in the determination of the appropriate behaviors and management approaches that would yield the success of an organisation both in the short-term and long-term basis. Organisational theory encompasses the study of organisations for the benefit of identifying common themes for the purpose of solving problems, maximizing efficiency and productivity, and meeting the needs of stakeholders. Topics such as environmental perspectives in enhancing organisational development, neoclassical perspectives, and classical perspectives of approaching organisational management are central to the study of organisational theory. From this perspective, organisational theory acts as a complement for studies in human resource coupled with organisational behaviors. Studying organisational behaviors is integral to the derivation of strategies for organisational management that would result to alignment of all organisational workers to common themes, goals, and objectives that spell out the reasons as to why an organisation is established. Without employees, an organisation cannot exist. For Continue reading
Key Performance Indicators (KPI) – Definition and Implementation
Meaning of Key Performance Indicators (KPI) Key Performance Indicators, abbreviated as KPI, are indicators that are used in an organization to define and measure company’s progress and how all operations are being carried out towards achievement of the already set goals by the organization. By Key performance indicators (KPI), the organization can judge its most critical aspects of organizational performance, and subsequently choose how to increase this performance. KPIs are non-financial, they are frequently measured, decided by the CEO and the higher-level management, require an understanding by the staff, provide responsibility, can significantly impact the organization, and have a positive effect on other measures. This comes in after an organization has laid down a well stated Mission and Vision. After that, goals are set whereby all the stakeholders in the organizational operations are involved. This is then followed by an analysis to see if these indicators are workable. This plays Continue reading
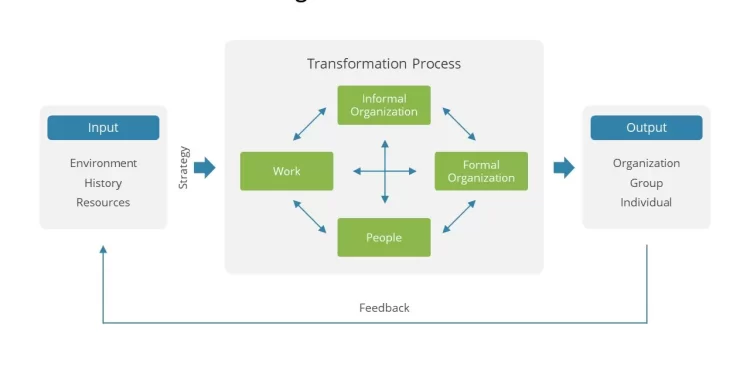
The Nadler-Tushman Congruence Model
The main responsibility of the management is to ensure smooth operations of a firm. In addition, the management must ensure that the goals being pursued by the organization are attained. Essentially, the goals of the organization can only be reached when the inputs are transformed into the final products and services. In other words, the major function of the management is to ensure that they put in place strategies that will ensure effective transformation of the organization’s inputs into the desired outputs. In addition, the management must also be efficient in all other operations related to the company’s functioning. However, managing the organization effectively has remained a challenge for the most of managers. Understanding the dynamics occurring within the organization including the group and individual behaviors, changing processes as well as the relationships that exist between the processes is complex . Despite the complexity of these processes, the changes occurring Continue reading
Advantages and Limitations of Prosci ADKAR Model
There are a number of models in management that aim to reduce resistance to change and control most organizational change processes. The Prosci ADKAR model is one of the best approaches introduced several years ago to support change in companies through the prism of its five major elements, namely awareness, desire, knowledge, ability, and reinforcement. The progress of the ADKAR model is evident today due to its evident advantages and the possibility to facilitate working processes. This model is developed from a study of 900 organizations across 59 countries over a 14-year period, carried out by the American research organization, Prosci. This model, developed by Jeff Hiatt, and first published in 2003, focuses on participatory approach of dealing with change. The model is simple to learn, makes sense, and focuses on the actions and outcomes required for change. ADKAR, in contrast to most other change management models, focuses on the human aspect Continue reading