In recent years, the conditions of competition in the global environment have changed for the companies. The market is dominated by constant change, complex tasks and environmental turbulence. As knowledge, innovation and flexibility become an important resource for sustained competitive advantage and ‘Entrepreneurship’ is the crucial factor for success or survival. While small firms take the advantage of these conditions and become very successful due to their flexible structure and entrepreneurial spirit, large firms suffer more due to their mechanistic, bureaucratic and rigid structures. One of the solutions for companies to deal with the rigid bureaucratic structures is to induce Corporate Entrepreneurship in their structure. While CEOs are concerned about profitable organic growth, they find corporate entrepreneurship or creating a new business as one of the solution. As corporate entrepreneurship is becoming popular, it can be seen as a school within entrepreneurship theory. Since there is no generally accepted definition Continue reading
Strategic Management Terms
Environmental Turbulence Concept in Strategic Management
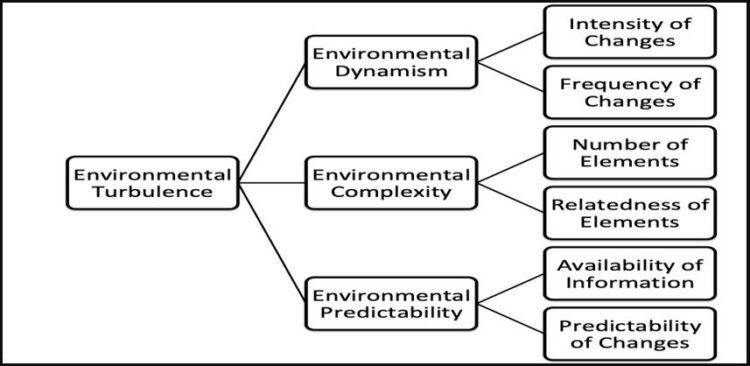
Business environments are described or analysed in various ways based on disparate important dimensions. However, the concept of turbulence is ambiguous. This confusion touches on the varying orientations in studying organisational environments and the diverse methods that are used to measure it. Environmental turbulence underscores the extent of change and degree of complexity in a business environment. Changes in technology, statutory regulations, or environmental factors are some of the examples that constitute environmental turbulence. Therefore, a turbulent environment is dynamic, expanding, unpredictable, and fluctuating. In addition, such an environment displays high levels of interconnectedness with the business. Turbulence is a complex interaction of several dimensions that are related to change where some elements dominate others or overlap each other at times. The figure below shows the configuration of the main dimensions of environmental turbulence. 1. Dynamism If the components of the tasks of the environment are highly variable, the business needs Continue reading
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) – Definition, Types, and Process
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) are increasingly becoming a novel approach for companies to wade through the competitive pressures of today’s globalized society. The increase of mega-mergers in today’s corporate world demonstrates the entrenchment of such transactions in modern business practices. Definitions of Mergers and Acquisitions “One plus one equals three”. This statement defines the main logic that informs merger and acquisition transactions. This logic stems from the fact that most companies aim to create a bigger shareholder value than the sum of the shareholder value that would ordinarily be realized if two corporate entities merge. The reasoning behind merger and acquisition transactions therefore stems from the fact that there is a greater value when two companies work together, as opposed to two companies working in isolation. Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) are therefore joint activities where the activities of two or more companies merge to create one common purpose for both Continue reading
Person-Environment Fit – A Theoretical Perspective
Organisational theory is essential in the determination of the appropriate behaviors and management approaches that would yield the success of an organisation both in the short-term and long-term basis. Organisational theory encompasses the study of organisations for the benefit of identifying common themes for the purpose of solving problems, maximizing efficiency and productivity, and meeting the needs of stakeholders. Topics such as environmental perspectives in enhancing organisational development, neoclassical perspectives, and classical perspectives of approaching organisational management are central to the study of organisational theory. From this perspective, organisational theory acts as a complement for studies in human resource coupled with organisational behaviors. Studying organisational behaviors is integral to the derivation of strategies for organisational management that would result to alignment of all organisational workers to common themes, goals, and objectives that spell out the reasons as to why an organisation is established. Without employees, an organisation cannot exist. For Continue reading
Unitarist Perspective Vs. Pluralist Perspective in Management
People have different ways of interpreting the events they come across in their daily life. School and family circumstances, encounters at the workplaces, clubs, religions, friends, society, and occupations influence most of the understandings. Employment is one of the elements that influence people’s life. Hence, management and the nature of employment are some of the issues that trigger heated debates. Generally, people have two different perspectives of interpreting managerial practices that take place at workplaces. These are known as unitarism and pluralism. The unitarist approach holds that workplace conflicts are avoidable. According to this approach, managers may detour them by bringing all the stakeholders together. They can and should make sure that an organization is managed from a single source of power. Meanwhile, pluralists hold that workplace conflicts are inevitable. Managers ought to convert them into profitable initiatives rather than criticize them. Unitarist Perspective Unitarists base their arguments on postulations that workplace conflict Continue reading
Business Risk Management – Meaning, Stages, Benefits and Limitations
Risk is the combination of the probability of an event and its impacts. It is the possibility of an event and its effect that constitute benefits or impediments to success in an undertaking. In an enterprise, identification of a hazard has both a helpful and a harmful aspects. Consequently, both the benefits and threats to the success of business operations are considered in the assessment of risk. When focusing on safety, risk only takes the perspective of negative consequences. As a result, it focuses on the alleviation and avoidance of harm. Threat management is vital in organizations’ tactical management. It entails a process where organizations tackle the risks connected to their actions with the objective of attaining constant benefit within individual activities and across a range of all actions. Businesses are affected by both interior and exterior factors relating to risks. Some risks can be categorized as external, while others Continue reading