A very commonly used term, globalization can mean different things to different people. At a broad level, globalization refers to the growing economic interdependence among countries, reflected in the increasing cross border flow of goods, services, capital and technical know how. At the level of a specific company, globalization refers to the degree to which competitive position is determined by the ability to leverage physical and intangible resources and market opportunities across countries. “Globalization refers to the multiplicity of linkages and interconnections between the states and societies that make up the present world system. It describes the process by which events, decisions, and activities in one part of the world come to have significant consequences for individuals and communities in quite distant parts of the globe. Globalization has two distinct phenomena: scope (or stretching) and intensity (or deepening). On the one hand, it defines a set of processes which embrace Continue reading
Strategic Management Terms
Strategic Planning – Meaning, Process and Approaches
Strategic planning is the process of deciding on the goals of the organization, on changes in these goals, on the resources used to attain these seals, and on the policies that are to govern the acquisition, use and disposition of these resources. The word strategy is used here in its usual sense of deciding on how to combine and employ resources. Thus strategic planning is a process having to with the formulation of long-range, strategic, policy-type plans that change the character or direction of the organization. In an industrial company, this includes planning that affects the goals of the company, policies of all types (including policies as to management control and other processes); the acquisition and disposition of major facilities, divisions, or subsidiaries, the markets to be served and distribution channels for serving them; the organization-structure (as distinguished from individual personnel actions); research and development of new product lines (as Continue reading
Strategic Thinking Dichotomies: Logical Thinking vs. Creative Thinking
It is mutually agreed that the converses of intuition and analysis generate tension during the strategic thinking process. Researchers and contributors to strategic management making the case for logic argue that for strategy to be effective, the strategic thinking process must involve extensive formal analyses and objective collection and processing of data both from within and without the corporation. Rational reasoning enables managers gain an accurate perspective on the different options available before identifying the strategic option that best serves the organization’s cause: achieving its goals and objectives. Logical analysis encompasses assessing internal and external risks, strengths and weaknesses, market need and so on; so that strategy can be thought out to fit each of the above factors. In contrast to logical thinking, creative thinking involves taking a “leap of imagination” without any logically defined reason for taking such a leap. Creative thinking is a divergence from the rules governing Continue reading
What is First Mover Advantage? Definition & Examples
In the business world that is characterized by cutthroat competition, businesses do whatever is in their capacity to gain a competitive advantage. One of the common desires for any business is to dominate an industry or a region by being the first to enter into the specific business area. As a business concept, first mover advantage is a highly preferred concept where businesses seek to dominate given business areas by being the pioneers. Although many examples show first mover advantage is not always the best, there are equally many success stories of being the pioneers in a given business area. Firstly, from a management viewpoint, any business that acquires customers in an area where other companies have not been established ends up being the market leader as the pioneer in the given business area. Such an organization has the technological leadership of the products it creates. The process of developing Continue reading
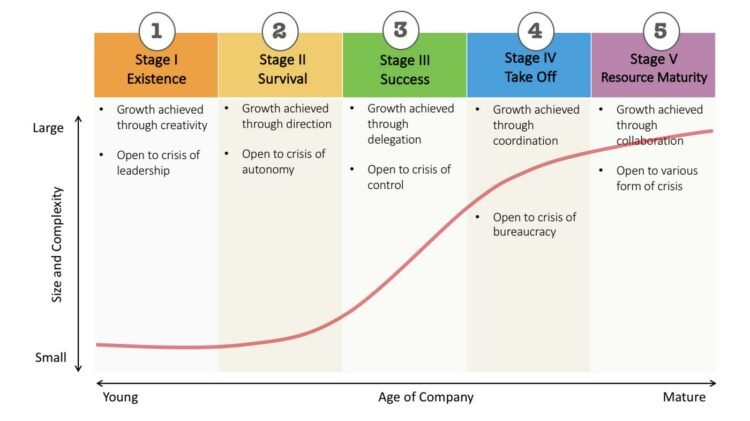
3 Important Models of Organisational Growth
An organization is a group of people who work together with coordinated efforts to achieve certain objectives or goals. Organisations are established by individuals or groups of individuals. During their formation, there is usually very little to talk about by the owner(s) and too much for them to do. Just like human beings, organisations need to grow so as to enable the owner or owners realize their objectives. If the aspect of growth is removed, then it becomes almost impossible for an organisation to exist beyond its formation stage. The signs of growth are expansion and increase in financial base. It also includes increase in the number of employees and diversification of a business as well as the separation of the owner from the business. Organisations also grow through mergers and acquisitions, all in the spirit of attaining their mission and vision. Business management commentators have described various models of organisational Continue reading
Firm That is Stuck in the Middle
The three Porters generic competitive strategies are alternative, viable approaches to dealing with the competitive forces. The converse of the previous discussion is that the firm failing to develop its strategy in at least one of the three directions – a firm that is stuck in the middle – is in an extremely poor strategic situation. According to Porter, a company’s failure to make a choice between cost leadership and differentiation essentially implies that the company is stuck in the middle. Porter argued that cost leadership and differentiation are such fundamentally contradictory strategies, requiring such different sets of resources, that any ï¬rm attempting to combine them would wind up “stuck in the middle” and fail to enjoy superior performance, Cost leadership requires standardized products with few unique or distinctive features or services so that costs are kept to a minimum. On the other hand, differentiation usually depends on offering customers Continue reading