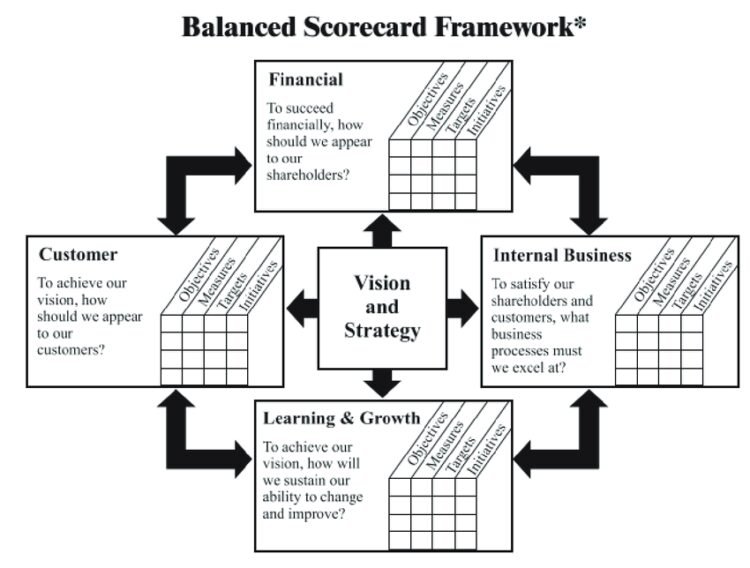
For modern organizations, it is essential to have methods for collecting data and making decisions based on the strategic objectives that lead to the achievement of competitive advantage. The balanced scorecard (BSC) represents strategic planning and management that companies use for communicating their intended accomplishments, aligning everyday procedures with the formulates strategy, monitoring progress, and prioritizing projects. In general, BSC is used for measuring and providing feedback to organizations, with data collection being crucial to the provision of quantitative results. This data is interpreted by managers and executives who make further decisions for an organization. The concept of Balanced Scorecard (BSC) was first introduced by Kaplan and Norton who received great praise for their research. The key principle behind the concept lies in finding balance across all functions of an organization since the majority of companies focus on financial measures such as growth and profitability, forgetting about such sectors as Continue reading
Strategic Management Tools
Relationship Between Firm Performance and Competitive Advantage
The firm performance is a complex term which may include different shadows of meaning as long as it relates to organizational performance, functioning of the firm and outcomes of its operations. Normally, the firm performance implies the organizational performance, including manufacturing of products and services, functioning of different units of the firm, performance of its employees and outcomes of their work in total. At the same time, the firm performance can be viewed in a broader context as a part of the business development of the firm. What is meant here is the fact that the business development mirrors the firm’s performance and allows to assess the extent to which the organizational performance is effective. At this point, it is important to place emphasis on the fact that the firm’s performance is basically measured in terms of efficiency of the firm’s operations. In fact, the more effective the firm’s operations Continue reading
Four Levels of Uncertainty – Strategic Planning Under Uncertainty
Even the most uncertain business environments contain a lot of strategically relevant information. First, it is often possible to identify clear trends, such as market demographics, that can help define potential demand for future products or services. Second, there is usually a host of factors that are currently unknown but that are in fact knowable-that could be known if the right analysis were done. The uncertainty that remains after the best possible analysis has been done is what we call residual uncertainty. Hugh G. Courtney, Jane Kirkland, and S. Patrick Viguerie in their article Strategy Under Uncertainty have developed a useful framework for dealing with various uncertainties in strategy formulation. Four Levels of Uncertainty The authors present four levels of uncertainty: 1) A predictable future, 2) Alternate futures 3) A range of futures 4) True ambiguity. Level 1: Clear Enough/Predictable Future This would apply to situations where sufficiently precise predictions Continue reading
Process Reengineering – History, Definition and Process Steps
The driving force behind all the changes which are taking place in the all the firm of the world are two Cs: customers, competition. The demands of the customers are changing day by day and this change in demand of customers pose new sets of challenges to the firms every now and then and hence firms have to change or modify their offering to customers accordingly. Firms who are able to do it in less time and less cost turn out to be the industry leaders. Firms set their mission and vision statements on the basis of their short term and long term strategy and to attain those goals firms need to adjust themselves with the constantly changing environment. We have seen dominance of Japanese firms in automobile and electronic components, the reason for this dominance of Japanese firms over other firms round the world is their techniques. They change Continue reading
Resource Based View (RBV) and Sustainable Competitive Advantage
Resource based view (RBV) focuses on the internal factors that contribute to a firm’s growth and performance. It highlights the importance of firm’s resources and capabilities. Both of them will together form a competency that can create a competitive advantage. Resources can also be divided into tangible resources and intangible resources. Capabilities of the firm in utilizing the resources have a big impact on how a firm will be able to stand out among other competitors. Competitive advantage arises when a firm has a lower cost structure, products differentiation and niche markets. RBV also concerns in value creation in order to compete with others. On the other hand, in order to survive in this competitive world, a firm needs to fully prepare itself to achieve sustainable competitive advantage (SCA), which means having a superior performance in a longer term compared to other rivals. According to Jay Barney (1991), resources need Continue reading
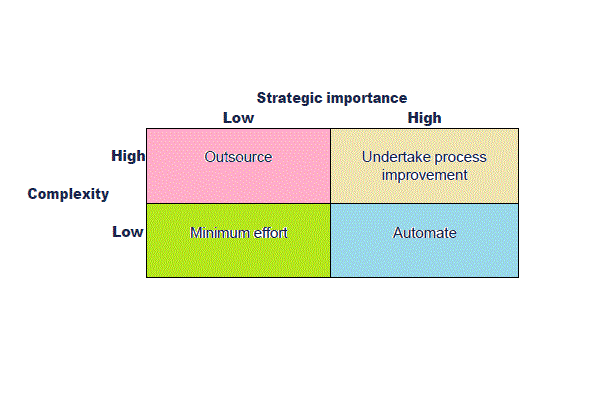
Harmon’s Process-Strategy Matrix
Process-Strategy matrix by Paul Harmon will be useful in deciding how the process should be managed, it gives two variable one Is importance and other is complexity and dynamics. There may be other variables to consider in practice such as culture, cost and savings and quality. It should be used flexibly by considering all the variable affecting the current and future prospects of the organization. Advantages and disadvantages should be considered before reaching the final decision. How To Assess The strategic Importance? Strategic importance can be assessed by asking what would happen if a process is abandoned. If it impacts the business objective (Quality, cost control and reputation etc.) materially (more than insignificant) than it can be assessed as high strategic importance like threatening to the survival of business. Strategic importance can also be assessed by identifying key stakeholders. If the process affecting the key stakeholders like customers, Tax authorities Continue reading