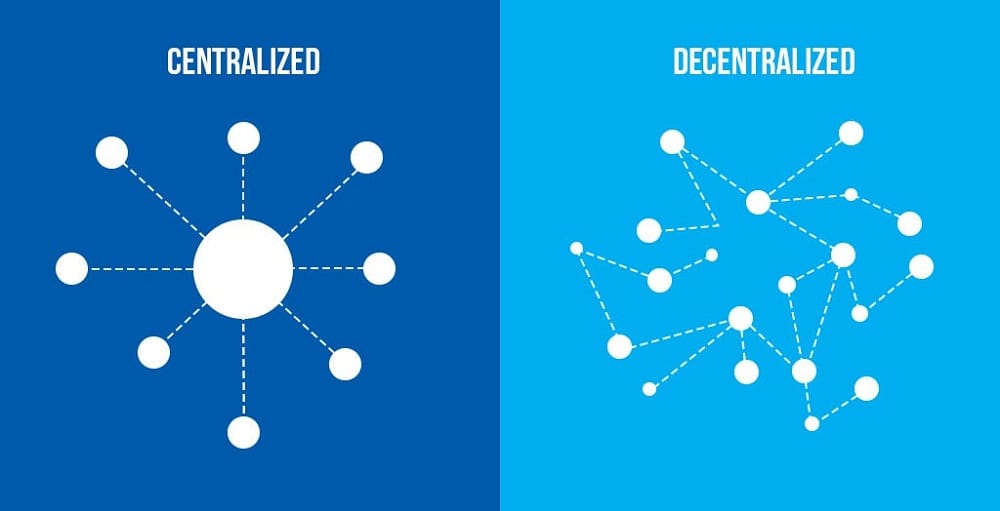
Decentralization is a defining characteristic of numerous cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based initiatives. By design, cryptocurrencies are decentralized and distributed, so there is no centralized authority or point of control. Decentralization in cryptocurrencies provides several benefits, including resistance to censorship and fraud, enhanced security, and better privacy. Decentralization carries several difficulties, particularly in terms of scalability and administration. Cryptocurrencies are a relatively young technology that is undergoing ongoing development.
Therefore, there is no universal approach to Decentralization. Each project must carefully consider the involved trade-offs to develop a system that works. Adopting Decentralization in cryptocurrency makes firms more resilient and secure and gives users greater control over their finances. The policy enables investors to make independent decisions because the firm’s directives are not dependent on a specific authority. Consequently, this develops a system of trust, as the system must rely on its integrity to sustain the company’s longevity in the market.
Decentralization of cryptocurrencies has been achieved from the systems’ first enterprise growth in response to market dynamics. As a result of the ability to use blockchain technology in cryptocurrency to reduce rents, most investors prefer these systems, thereby establishing the autonomy of blockchain technology. The new financial architecture eliminates middle management and team member authority to make decisions and provide organizational solutions. By involving all stakeholders, the corporation can decentralize its activities, resulting in organizational growth and opportunity for the business. The success of Decentralization has been ensured by allowing middle-level managers and team members to focus solely on their areas of expertise, such as customer insights and business objectives.
Firms have successfully achieved Decentralization by establishing values and culture that serve as a foundation and guide for their stakeholders. This creates a strong culture in the workplace by restoring and reinforcing the company’s values, allowing the company to achieve Decentralization. By prioritizing openness in communication, cryptocurrency-related businesses have established a relationship between customers and staff to facilitate collaboration on business operations. This has allowed the company to create Decentralization.
Cryptocurrency-related businesses have achieved Decentralization due to the all-inclusive nature of their workforce’s. Diversity in thoughts and decision-making has resulted from the inclusiveness of employees. This is accomplished by interviewing employees, consumers, and stakeholders. This has enabled businesses to have a deeper understanding of particular issues, helping them to make well-informed choices. Employers are able to prioritize training that helps employees grasp their jobs, roles, and expectations due to the inclusiveness of their workforce. The training programs have provided employees with a deeper understanding of the firm’s culture and management, enabling them to meet company expectations and foster a healthy working culture. This has thus enabled cryptocurrency-related businesses to attain Decentralization.
Different cryptographic strategies, like hash functions and zero-knowledge protocols, have enabled businesses to achieve Decentralization. For instance, using key rotations in everyday operations has reduced the likelihood of data compromise. The frequent rotation of master keys on the firm’s key stakeholders enables the development of secure information that safeguards the information. Thus, this aids the company in preventing data phishing and cyber-crimes, enabling it to attain Decentralization.
Various network architectures have been developed to ensure the Decentralization of data ownership in cryptographic procedures. For instance, network design’s peer-to-peer (P2P) architecture provides data decentralization without using intermediaries. By distributing tasks among its nodes and peers, the network architecture enables the transfer of digital currency from user to user via blockchain integration. Consequently, with the aid of a decentralized blockchain, p2p designs can achieve irreversible transactions. The network nodes are equipped with ledgers that distribute information. The nodes function by replication and ledger duplication. This aids in attaining Decentralization by decreasing trust costs and government support, as well as the need for agents, clerks, and other authorities such as assent officers. Each transaction’s consensus and immutability are not dependent on centralized entities such as governments. Thus, this provides Internet of Things (IoT) systems with a security solution.
Using a distributed Hash table (DHT) permits businesses to store data using vital data-based pairs. The distributed hash table nodes constitute a decentralized collaborative structure. The created systems are fault-tolerant, allowing them to handle several information nodes. The capacity to support many nodes equips the systems with massive amounts of data in any desired format. The DHT nodes are easily removable and extensible, facilitating data re-balancing in system clusters. Interplanetary File Systems (IPFS) are decentralized and designed to store and combine data in a decentralized manner as part of cryptographic processes. This helps the company discover difficulties and maintain data records that guarantee security.
In addition, it is claimed that Decentralization in hash functions is achieved by distributing the hashing algorithm across multiple network nodes, as opposed to having a centralized entity perform the hashing. This makes the hashing process more resistant to attacks, as an attacker must compromise multiple nodes to alter the hash output. Merkle tree is utilized in hash functions to decentralize them. Each node in a Merkle tree contains a hash of the data it is responsible for. The tree’s root then contains a hash of Merkle trees are frequently employed in cryptocurrency systems because they enable efficient and secure verification of data (such as transaction histories) without requiring storage of the entire data set.
Numerous information-protection features, such as the usage of anonymous usernames and user profiles, ensure adequate security for a user’s personal information. Zero-knowledge protocols, which allow data to be shared without revealing any information about it, provide a more flexible approach. This is accomplished by allowing two parties to share data without decryption, making it more efficient than homomorphic encryption.
In addition, because zero-knowledge protocols are decentralized, they do not necessitate data storage in a centralized location. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) provide data security for the zero-knowledge protocol. SSL and TLS provide confidentiality and data integrity between communication applications. They prevent man-in-the-middle attacks and eavesdropping, tampering, and forgery of the communication’s content. SSL and TLS use asymmetric encryption methods to generate a secret key that is exchanged between two parties. Asymmetric encryption makes use of a pair of public and private keys. Only the corresponding private key can decrypt anything encrypted with the public key. This ensures that neither party has access to the secret key. Message authentication codes (MAC) are utilized by the two applications to ensure data integrity. A MAC algorithm computes a hash value using a secret key. The hash is used to ensure the integrity of the message. In addition, SSL and TLS use digital certificates to validate the server and client’s identities. This enables cryptographic processes to safeguard data, thereby facilitating Decentralization.
Additionally, zero knowledge ensures data decentralization by guaranteeing appropriate data storage on computers, hard disk drives, or servers. Data is saved in a file that separates the data and stores it on many servers, requiring the development of a signature containing information about each component. The zero-knowledge protocol ensures that the signature is stored in a location distinct from where the data parts are stored and that the signature can be reconstructed using a data verification checklist.
In addition, Decentralization in blockchain initiatives has enabled firms to resist censorship and fraud, enhance security and better privacy. Firms consider using tradeoff systems that make them more resilient and secure. Firms have utilized Decentralization by adopting policies and strategies like hash functions and zero-knowledge protocols. These strategies have enabled firms to establish and develop secured systems that protect their data against data phishing and cybercrimes.