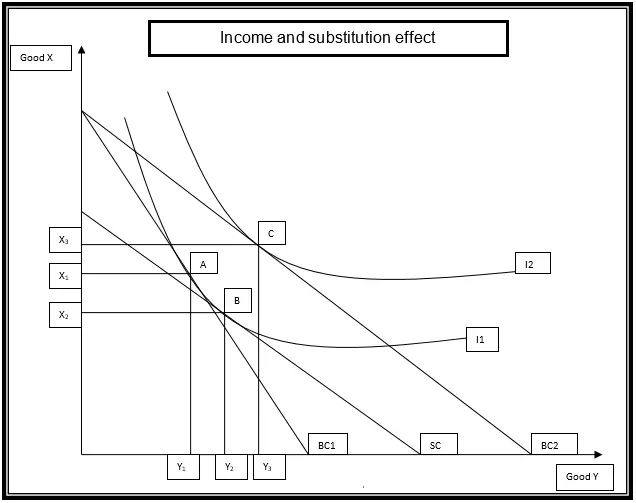
There’s No Such Thing as a Free Lunch – Discussion
Economists make a statement that there is nothing like free lunch and this is a fact. It should be known that this is a popular adage that has been used to communicate economic aspects for a long period of time. In this case, economists are just saying that it is literally impossible for an individual to get something for free without giving out anything. This means that you can not expect to get something for nothing. There has been an argument that this phrase is the core of economics which is undisputable. The whole issue of free lunch can be evaluated and looked at from different perspectives depending on the prevailing situation. For instance, we can look at this aspect from an opportunity cost point of view whereby an individual will be expected to trade off one thing for the other. This means that a decision has to be made as Continue reading