Understanding Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI)
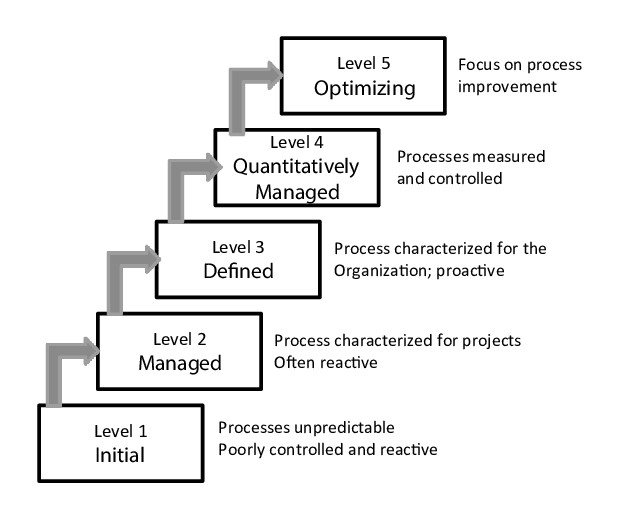
The Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) is a popular framework for evaluating or appraising where an organization’s maturity ranks within a defined program. The CMMI could show where an organizational program is ad-hoc and unorganized as compared to a highly structured and repeatable program. The CMMI was originally developed by the Software Engineering Institute, a cohort of government groups, and industry experts. The CMMI was originally designed to have an application towards software engineering but was quickly generalized to other areas of program appraisal. In January of 2013, the CMMI Institute was formed at Carnegie Mellon to continue the research and dissemination of the framework. Practitioners should take notice that the CMMI is not a standard and does not provide detailed information about achieving the goals being measured. The framework was more designed to serve as a guideline to understanding current implementations and alternative mechanisms to implement maturity levels in Continue reading