Case Study: The Lego Group and Its Sacred Cows
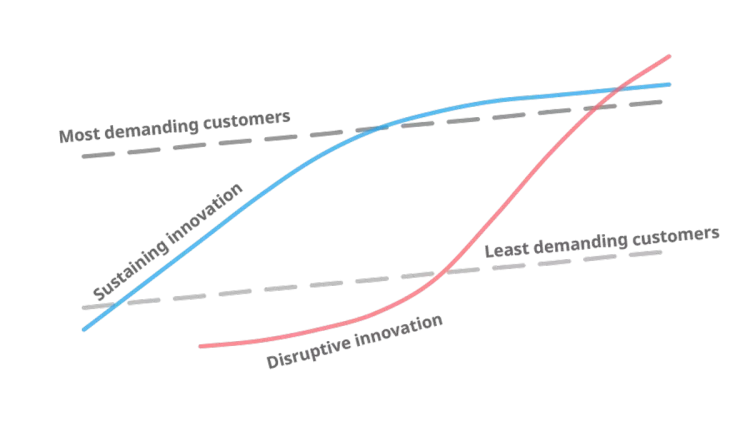
The ability to adapt to the changing environment, customer demands, and market forces is vital to the success of a business. The mindset and practices that have propelled a company to success are not necessarily the ones that would help stay successful in the future. It is often advisable to discard the elements that drag the company down, even if they have been a part of it for half a century. These elements can be regarded as metaphorical sacred cows, which are expected to be exempt from any form of metaphorical animal cruelty. This irrational reverence can make a business go bankrupt before giving up on the familiar but obsolete practices. That exact fate almost befell LEGO, one of the most recognizable toy manufacturers in the world. Only through cutting the unnecessary ideas and changing the litigious mindset could the company save itself from the brink of ruin. Case Background Continue reading