The Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) is a popular framework for evaluating or appraising where an organization’s maturity ranks within a defined program. The CMMI could show where an organizational program is ad-hoc and unorganized as compared to a highly structured and repeatable program. The CMMI was originally developed by the Software Engineering Institute, a cohort of government groups, and industry experts. The CMMI was originally designed to have an application towards software engineering but was quickly generalized to other areas of program appraisal. In January of 2013, the CMMI Institute was formed at Carnegie Mellon to continue the research and dissemination of the framework. Practitioners should take notice that the CMMI is not a standard and does not provide detailed information about achieving the goals being measured. The framework was more designed to serve as a guideline to understanding current implementations and alternative mechanisms to implement maturity levels in the program.
Defining the CMMI Levels
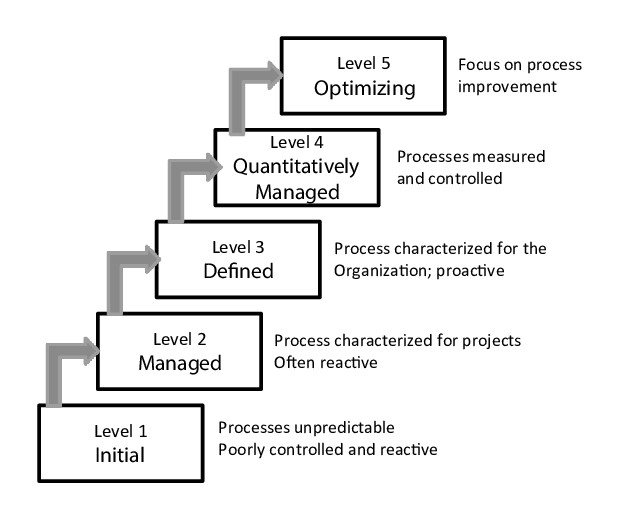
The Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) defines a capability model method to measure levels across the framework. The five maturity levels are defined as initial, managed, defined, quantitatively managed, and optimizing. The CMMI framework offers a statistical means for organizational management to rank and understands how to improve the process being evaluated. A CMM should provide guidance on what actions can be performed to improve the process rather than explicitly listing steps to achieve the next level of maturity. As the organization capability increases, the results produced will better align with expectations and accuracy. As results improve from the CMM, an organization should experience decreased costs, decreased development time, increased productivity and increased quality.
- CMMI level 0 is defined as incomplete. At level 0, processes are not executed or are executed incorrectly. Processes are executed with no goals and without clear standards.
- CMMI level 1 is defined as performed. At level 1 processes are chaotic and ad hoc. At this level, an organization would not expect a stable outcome and productive activities at this level are attributed to the experience of the person or team involved. Organizations at this initial level would not expect a quality outcome from this process.
- CMMI level 2 is defined as managed. Visibility has been provided for management to understand the status of the processes and controls are in place. At the managed level, services are expected to follow project plans that meet standards and requirements.
- CMMI level 3 is labeled as defined. At the level the defined level, processes are clearly understood, documented, followed, and consistent. Defined mature processes are improved by the attributes of greater detail, proactive quality controls, deeper understanding of relationships, and detailed metrics.
- CMMI level 4 is defined as quantitatively managed. This level exhibits a program by which subprocesses are reviewed by statistical means to improve control over the larger processes. Detailed measurements are collected and analyzed. Variations would be identified and analyzed for improvements to quality. Level 4 processes are more mature than a level 3 processes by the quantitative measurements that are taken and used for decision-making.
- CMMI level 5 is optimized. At level 5 processes are continually improved through technology innovation. Improvements are measured and evaluated. The organization’s ability to quickly impart change as opportunities is a result of a cycle of constant process improvement. Level 5 processes are at a higher maturity because of the analysis of variations and predictability.
CMMI maturity levels cannot be skipped or passed over. The more mature levels are built on the success of the lower levels. The CMMI Institute claims that an organization at a lower maturity level can attempt to perform processes at a higher level but must understand that there is a risk of inconsistency. Overall, the CMMI provides an easy framework that can be modified to fit most organizational management situations.