Different companies, similarly to people, have their own unique culture that is founded on ethnic, regional, temporal and industry-relevant factors. Therefore, when two or more businesses work together or decide to merge, these specific attributes may clash, leading to conflicts and worsened performance outcomes. The process of acquisition has to be planned in detail from the first contact between the companies to their full integration. In most successful cases, firms prepare thoroughly to enter the new relationship by mapping out the process of the merger and trying to predict the potential issues. However, the importance of the steps following the official merger may be overlooked by managers who fail to account for the fundamental cultural and structural differences between the businesses. In foreign mergers, this lack of attention to the whole strategy may be detrimental to the outcome of the project. This problem is especially evident for cultures that have Continue reading
Corporate Strategies
What is First Mover Advantage? Definition & Examples
In the business world that is characterized by cutthroat competition, businesses do whatever is in their capacity to gain a competitive advantage. One of the common desires for any business is to dominate an industry or a region by being the first to enter into the specific business area. As a business concept, first mover advantage is a highly preferred concept where businesses seek to dominate given business areas by being the pioneers. Although many examples show first mover advantage is not always the best, there are equally many success stories of being the pioneers in a given business area. Firstly, from a management viewpoint, any business that acquires customers in an area where other companies have not been established ends up being the market leader as the pioneer in the given business area. Such an organization has the technological leadership of the products it creates. The process of developing Continue reading
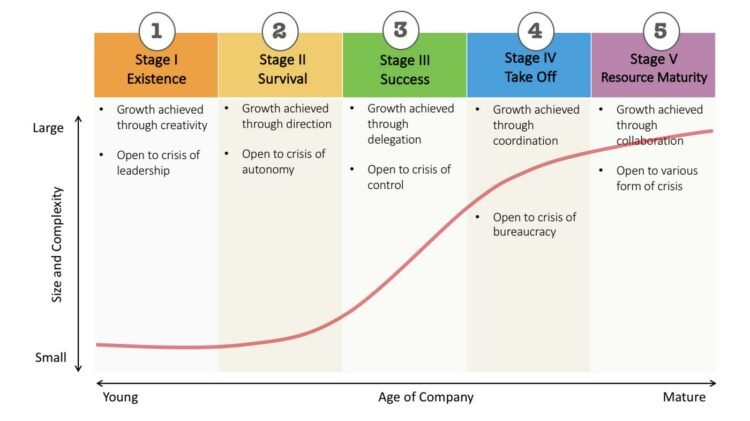
3 Important Models of Organisational Growth
An organization is a group of people who work together with coordinated efforts to achieve certain objectives or goals. Organisations are established by individuals or groups of individuals. During their formation, there is usually very little to talk about by the owner(s) and too much for them to do. Just like human beings, organisations need to grow so as to enable the owner or owners realize their objectives. If the aspect of growth is removed, then it becomes almost impossible for an organisation to exist beyond its formation stage. The signs of growth are expansion and increase in financial base. It also includes increase in the number of employees and diversification of a business as well as the separation of the owner from the business. Organisations also grow through mergers and acquisitions, all in the spirit of attaining their mission and vision. Business management commentators have described various models of organisational Continue reading
Innovation in Large versus Small Firms
In 1940s, Austrian economist Joseph Schumpeter argued that large firms would be more effective innovators and he point out that better able to obtain financing for R&D projects and better able to spread costs of R&D over large volume. Large size firms may also enable for greater economies of scale and learning effect and taking on large scale or risky projects. However, large firms might also be disadvantaged at innovation because; R&D efficiency might decrease due to loss of managerial control Large firms have more bureaucratic inertia More strategic commitments tie firm to current technologies Small firms often considered more flexible and entrepreneurial. Many big firms have found ways of “feeling small” because break overall firm into several sub-units and can utilize different culture and controls in different units. A large firm gains experience in choosing and developing innovation projects, it may learn to make better selections of projects that Continue reading
Analysis of Competitive Position Using Porter’s Five Forces Model
Michael Porter’s Five-Forces Model of competitive analysis is a widely used approach for developing strategies in many industries as the intensity of competition among firms varies widely across industries. According to Porter, the nature of competitiveness in an industry can be viewed as a composite of five forces: rivalry among competing firms, potential entry of new competitors, potential development of substitute products, bargaining power of suppliers and bargaining power of consumers. There are 3 steps to use Porter’s Five Forces Model can reveal whether competition in a given industry is such that the firm can make an acceptable profit. Firstly, identify key aspects or elements of each competitive force that impact the firm. Secondly, evaluate how strong and important each element is for the firm. Lastly, decide whether the collective strength of the elements is worth the firm entering or staying in the industry. Rivalry among the competing firms is Continue reading
Case Study: The Hewlett-Packard and Compaq Merger
The following is a brief description of the two companies: Hewlett-Packard (HP) It all began in the year 1938 when two electrical engineering graduates from Stanford University called William Hewlett and David Packard started their business in a garage in Palo Alto. In a year’s time, the partnership called Hewlett-Packard was made and by the year 1947, HP was incorporated. The company has been prospering ever since as its profits grew from five and half million dollars in 1951 to about 3 billion dollars in 1981. The pace of growth knew no bounds as HP’s net revenue went up to 42 billion dollars in 1997. Starting with manufacturing audio oscillators, the company made its first computer in the year 1966 and it was by 1972 that it introduced the concept of personal computing by a calculator first which was further advanced into a personal computer in the year 1980. The Continue reading