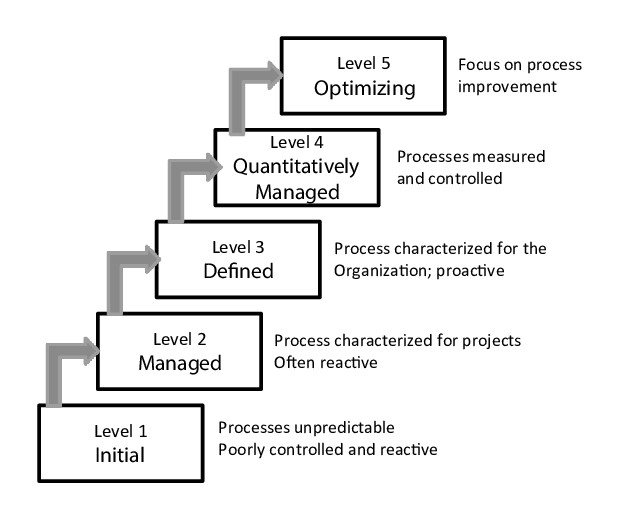
The Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) is a popular framework for evaluating or appraising where an organization’s maturity ranks within a defined program. The CMMI could show where an organizational program is ad-hoc and unorganized as compared to a highly structured and repeatable program. The CMMI was originally developed by the Software Engineering Institute, a cohort of government groups, and industry experts. The CMMI was originally designed to have an application towards software engineering but was quickly generalized to other areas of program appraisal. In January of 2013, the CMMI Institute was formed at Carnegie Mellon to continue the research and dissemination of the framework. Practitioners should take notice that the CMMI is not a standard and does not provide detailed information about achieving the goals being measured. The framework was more designed to serve as a guideline to understanding current implementations and alternative mechanisms to implement maturity levels in Continue reading
Project Management
Procurement Methods in Project Management
The development of procurement strategy follows the stages in the life of a project. Initially, a preliminary strategy is determined. It is based on a broad definition of objectives and is an essential step in establishing the way forward for the project. It encourages the client to consider strategy early. The preliminary procurement strategy is usually developed with help from the client’s adviser and possibly other consultants. Procurement strategy development has three components: Analysis – assessing and setting the priorities of the project objectives and requirements; Choice – considering possible options, evaluating them and selecting the most appropriate; and Implementation – putting the chosen strategy into effect. During strategy preparation, it may be necessary to seek specialist advice from other consultants, for example, in relation to expected costs for the project. The adviser should advise the client on this. Specialist advice should besought when developing the strategy for novel or Continue reading
PRINCE2 Methodology in Project Management
PRINCE2 is one of the world’s most widely used project management methodology. It was originally developed for UK government IT projects, its use has been widened to large projects of all kinds, and it has been taken up internationally in more countries in both public and private sectors such as police forces, telecommunication companies, banks, as well as other large commercial organisations and also used in enterprise resource planning implementations. PRINCE2 stands for Projects in Controlled Environment and it was developed at a time when the UK government was outsourcing an increasing amount of its work, and the methodology incorporates best practice on the integration of internal teams and external agencies. PRINCE2 takes a process approach to project management, fitting each process in to a framework of essential components that need to be applied throughout the project. PRINCE2 focuses mainly on the aspects of managing projects in the life cycle Continue reading
Essential Skills for Project Managers
To be a good project manager, it is important to possess several skills in order to manage the project in the organization. Project managers need to have a wide variety of skills which can help them to do the best in project management. All the skills that possess by the project manager is determinant of the success of the project in project management. It is to fulfill the responsibilities as the project manager. There are several major knowledge and skill categories for project manager. Skills requirement of the project manager divided into four categories. Below are the four major knowledge and skills categories of the project manager. Project management process skills: Project Management process skills are the knowledge and skills related to the mechanism of project management. The project manager should be knowledgeable about tools, techniques and process technology in project management as well able to apply them in real Continue reading
Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
In the critical path method of scheduling projects, the duration of each activity is usually defined with a reasonable degree of certainty. For some projects, it may be difficult to estimate a reasonable single duration for one more of the activities in the project schedule. The Program Evaluation and Review Technique or PERT method of project scheduling, uses three durations for each activity and the fundamental statistics to determine the probability of a project finishing earlier or later than expected. Although the PERT method is not used extensively in engineering and construction projects, it provides valuable information for assessing the risks of a schedule slippage in a project. Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) was first developed in 1958 by the U.S. Navy Special Projects Office on the Polaris missile system. Existing integrated planning on such a large scale was deemed inadequate, so the Navy pulled in the Continue reading
Reasons and Advantages of Using Special Purpose Vehicles in Project Financing
A special purpose vehicle refers to a firm whose operations are limited to the acquisition and financing of specific assets or projects. SPVs are usually established as subsidiaries whose assets and liabilities are structured in a manner that makes their obligations secure irrespective of the financial difficulties of their parent companies. Thus, a special purpose vehicle will be necessary to generate adequate funds to complete the project. Project financing refers to the raising of funds on a limited recourse basis for the purposes of developing a large-scale capital intensive project through a special purpose vehicle. Generally, the borrowed funds are often repaid using the revenue from the project. Reasons of Using SPVs in Project Financing One of the main reasons for using SPVs is to share the risks associated with implementing large-scale infrastructure projects with the financiers. SPVs are often formed as independent legal entities with several shareholders. The common Continue reading